security
DDoS
What it is?
- Attacks designed to overload websites
- Compete against legitimate connections
- Distributed - hard to block individual IPs/Ranges
- Often involve large armies of compromised machines - botnets
Category
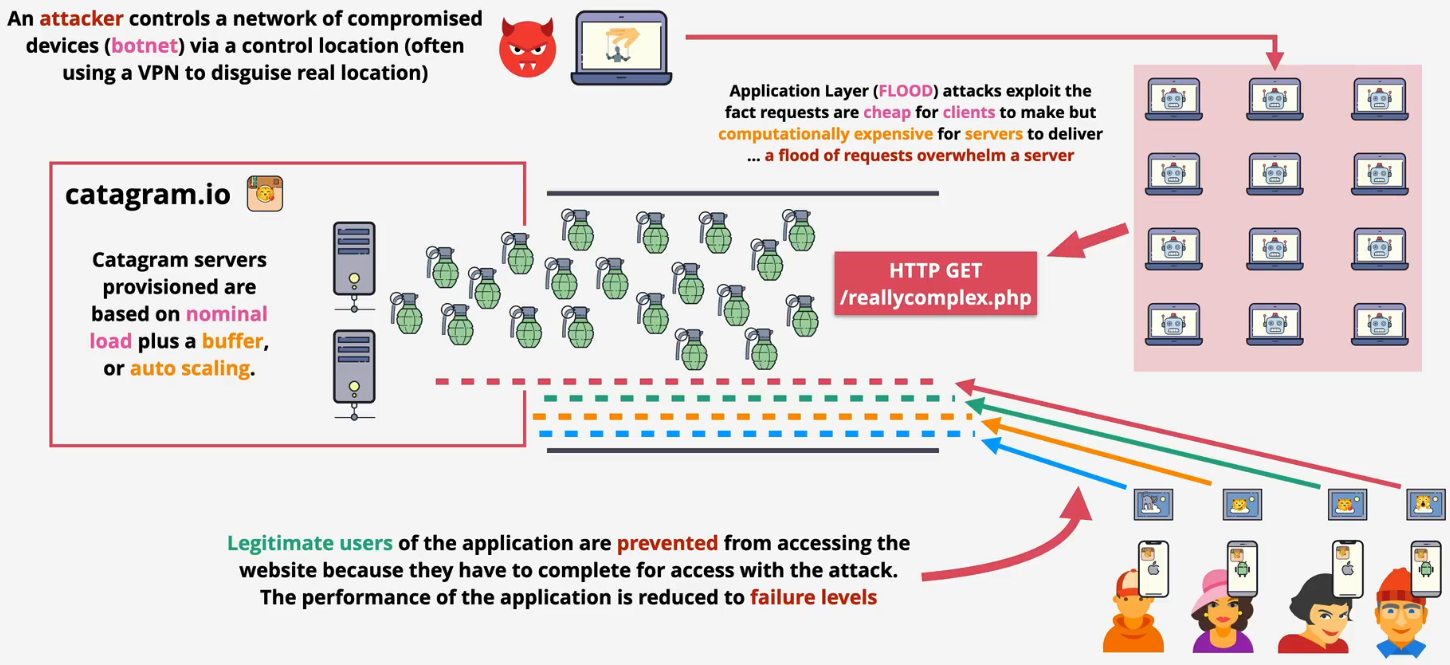
- Application layer - HTTP flood
- Sending a massive number of seemingly legitimate requests, such as repeated asking for a webpage or trying to log in
- The goal is to exhaust the server's resources (like CPI and memory), causing it to crash or become too slow to server actual users
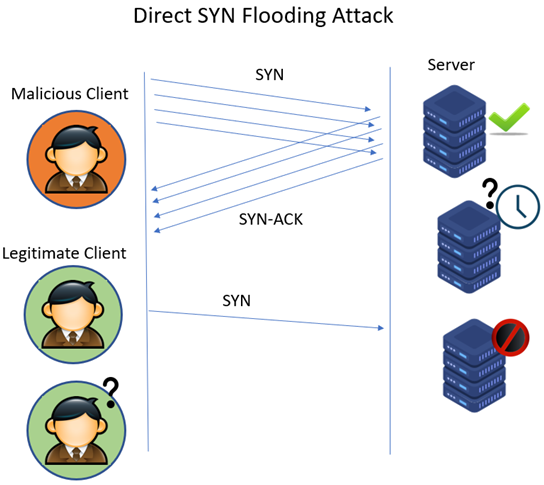
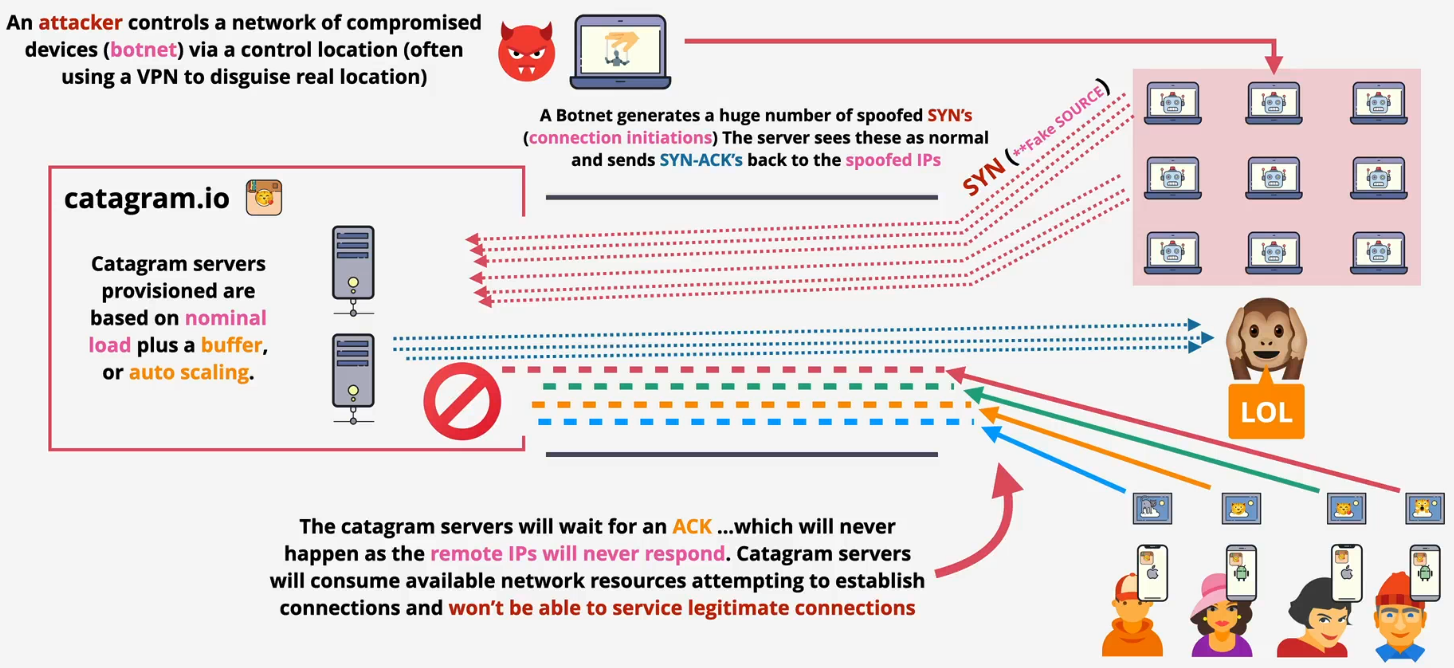
- Protocol attack - SNYK flood
- Sending a flood of "SNY" requests to a server to initiate a connection but never completes the process. The server is left waiting for a response that never arrives
- Eventually, the server runs out of available spots to hold for new connections and legitimate users are blocked from connecting
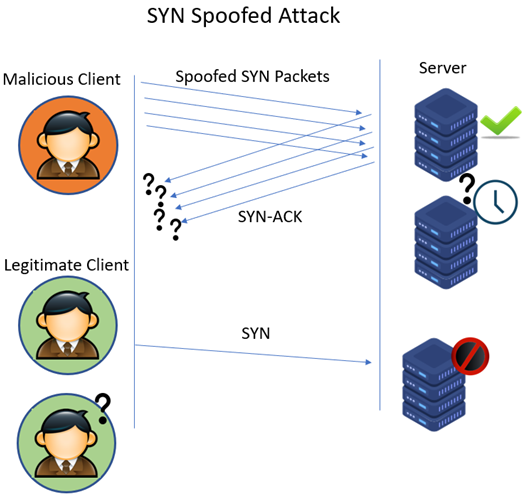
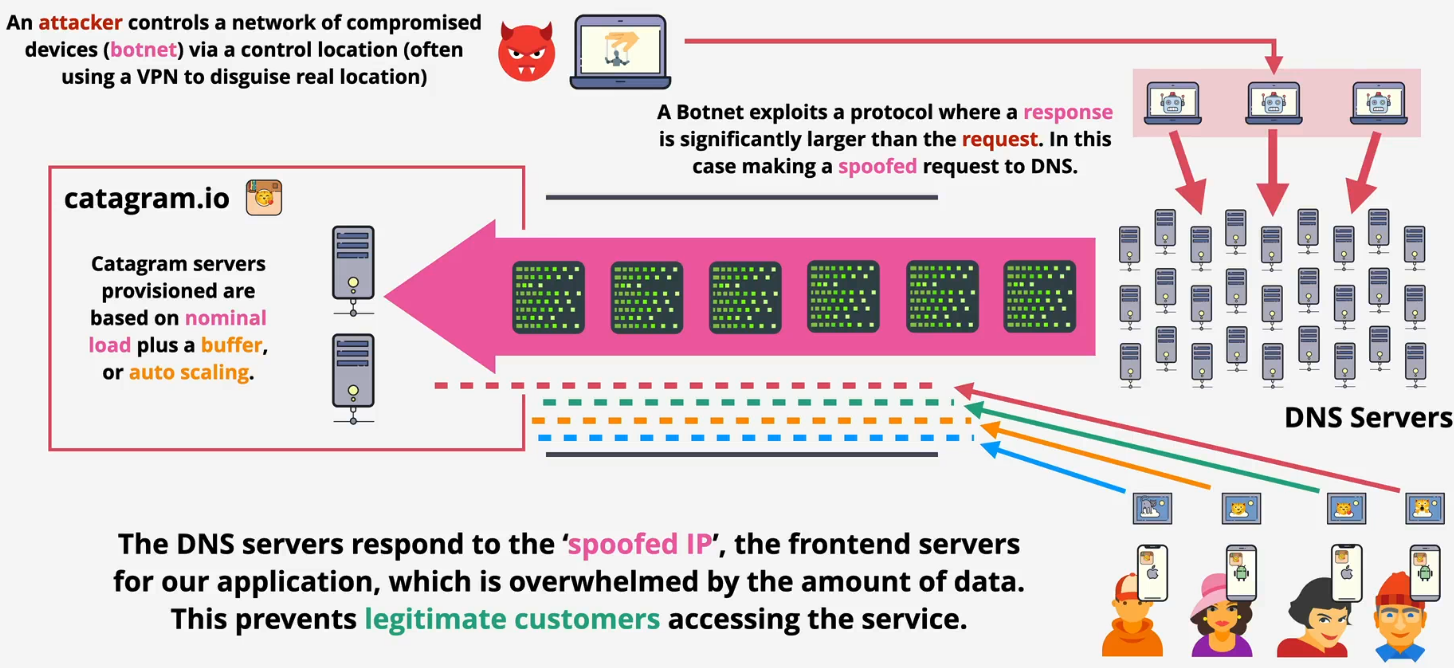
- Volumetric - DNS amplification
- Sending small requests to public DNS servers but spoofs the return address to be the victim's IP address
Cases
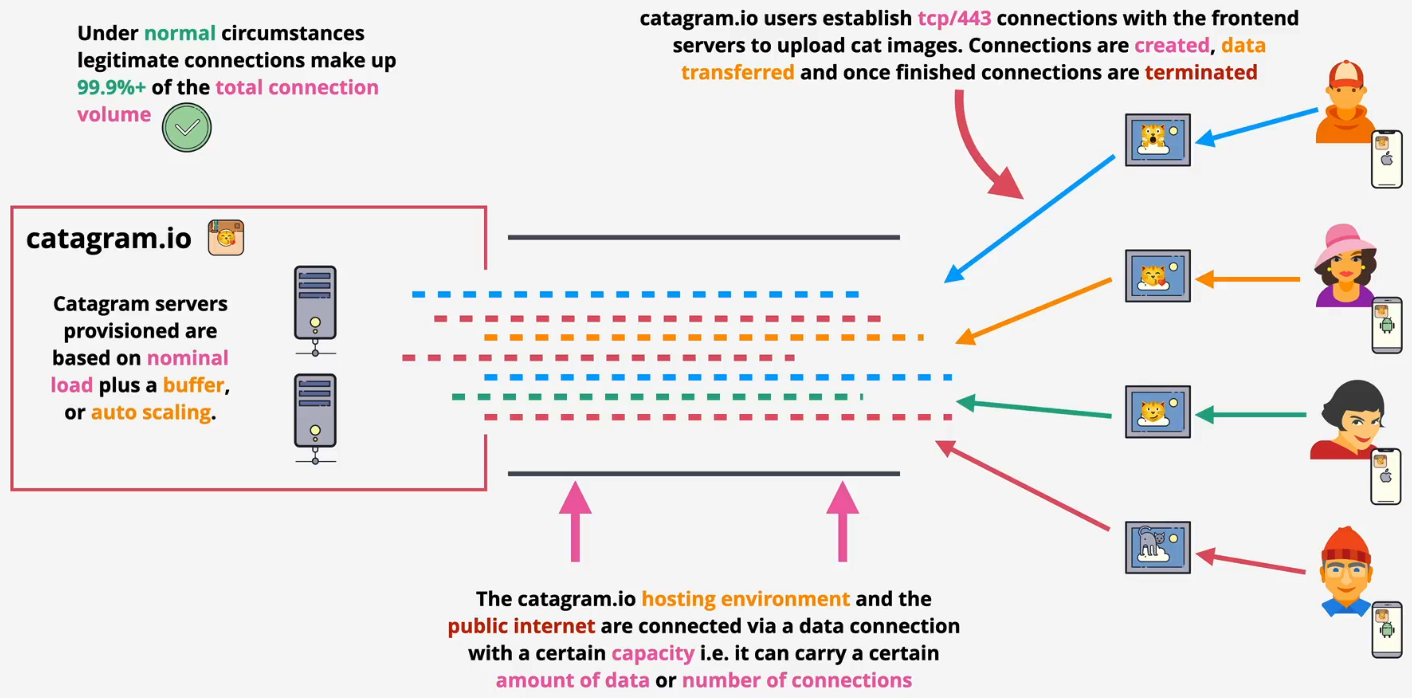
- Normal
- Application layer
- Protocol attack
- Volumetric
SSL and TLS
What is it?
- SSL - Secure Sockets Layer and TLS - Transport Layer Security
- TLS is a newer and more secure version of SSL
- Provide privacy and data integrity between client and server
- Privacy: Communications are encrypted. It could be asymmetric and then symmetric
- Identity (server of client/server) verified
- Reliable connection: Protect against alteration
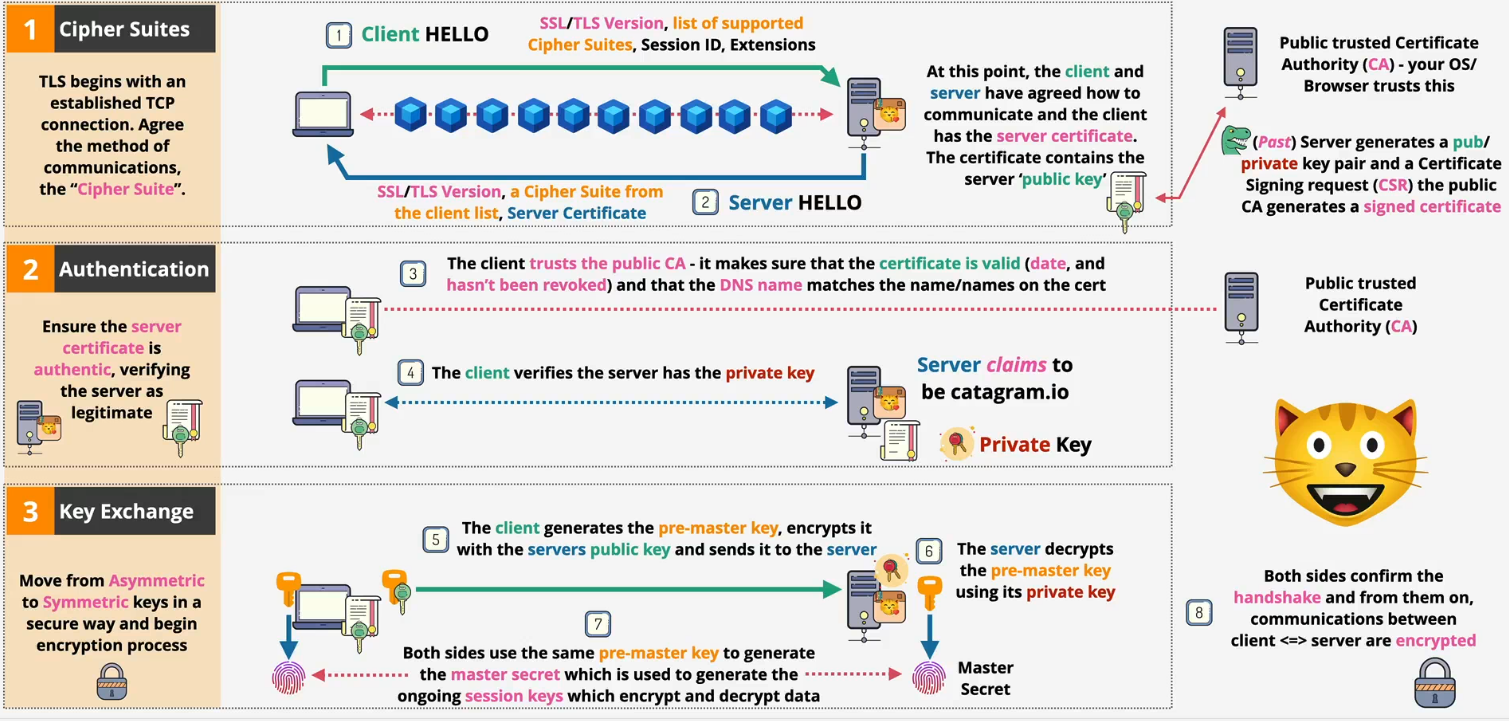
Architecture
- Server certificate issuance flow
- Generate a key pair: The server owner creates a public key (which will be shared) and a private key (which is kept secret)
- Create a CSR: They create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). This is essentially an application form that includes the public key and identifying information (like the domain name)
- Submit to the CA: The CSR is sent to a trusted Certificate Authority (CA)
- CA verifies ownership: The CA performs validation to ensure the applicant actually owns the domain they're requesting the certificate for
- CA signs and issues the certificate: Once verified, the CA uses its own private key to digitally sign the CSR. This act of signing officially creates the SSL certificate
- Certificate is returned: The final, signed certificate—which now contains the server's public key and the CA's trusted signature—is sent back to the owner
- Install on server: The owner installs this new certificate and their original private key on the web server, making it ready to accept secure connections
- Phase 3: Exchange
- The client generates a pre-master secret and encrypts it using the server's public key
- The server decrypts the encrypted pre-master secret using its private key
- Both sides use the shared pre-master secret to generate a master secret. This is then used to create the session keys, which encrypt and decrypt all application data (like your browsing activity) for the rest of the session
Hashing
What is it?
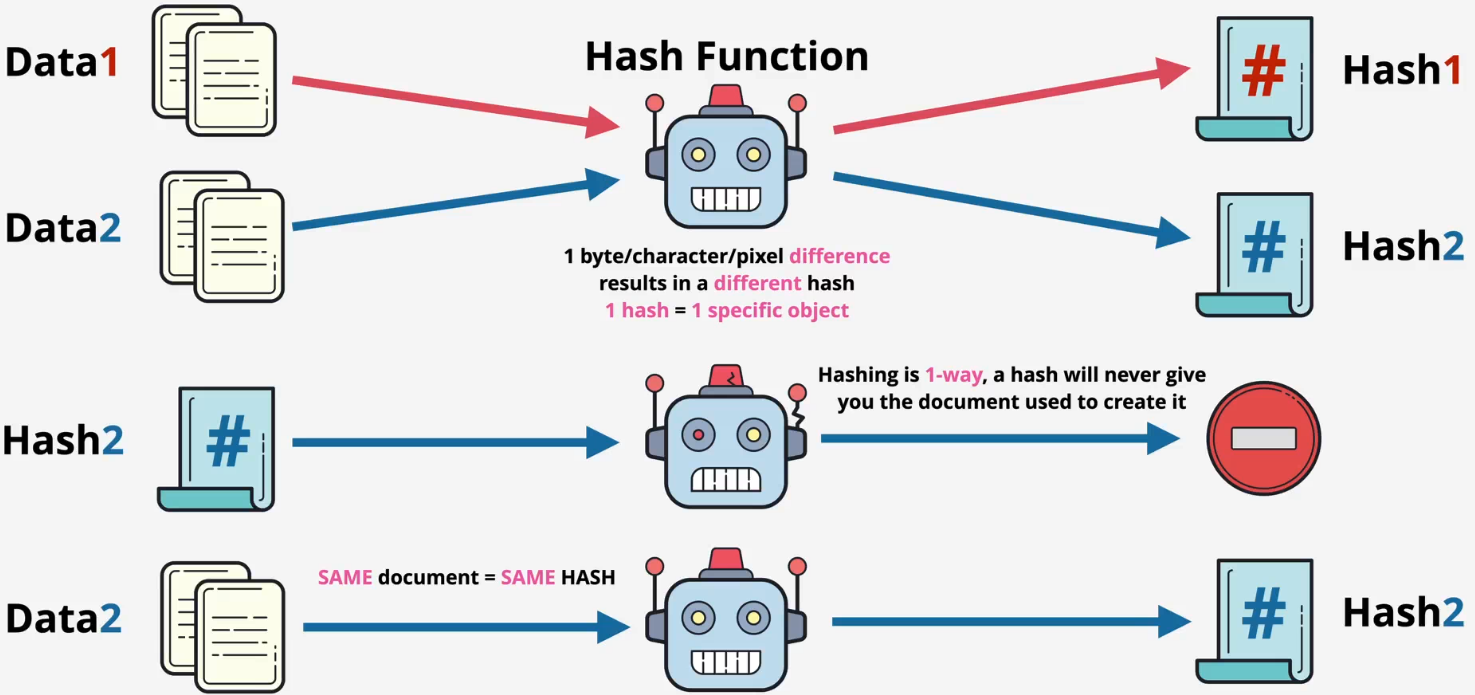
- Data + Hashing function → Hash
- You cannot get the original data from a hash
- Same data = same hash
- Different data = different hash
- Downloaded data can be verified by using hash
- You can take data, hash it, and compare the hashesfa
- If so, the downloaded data is unaltered
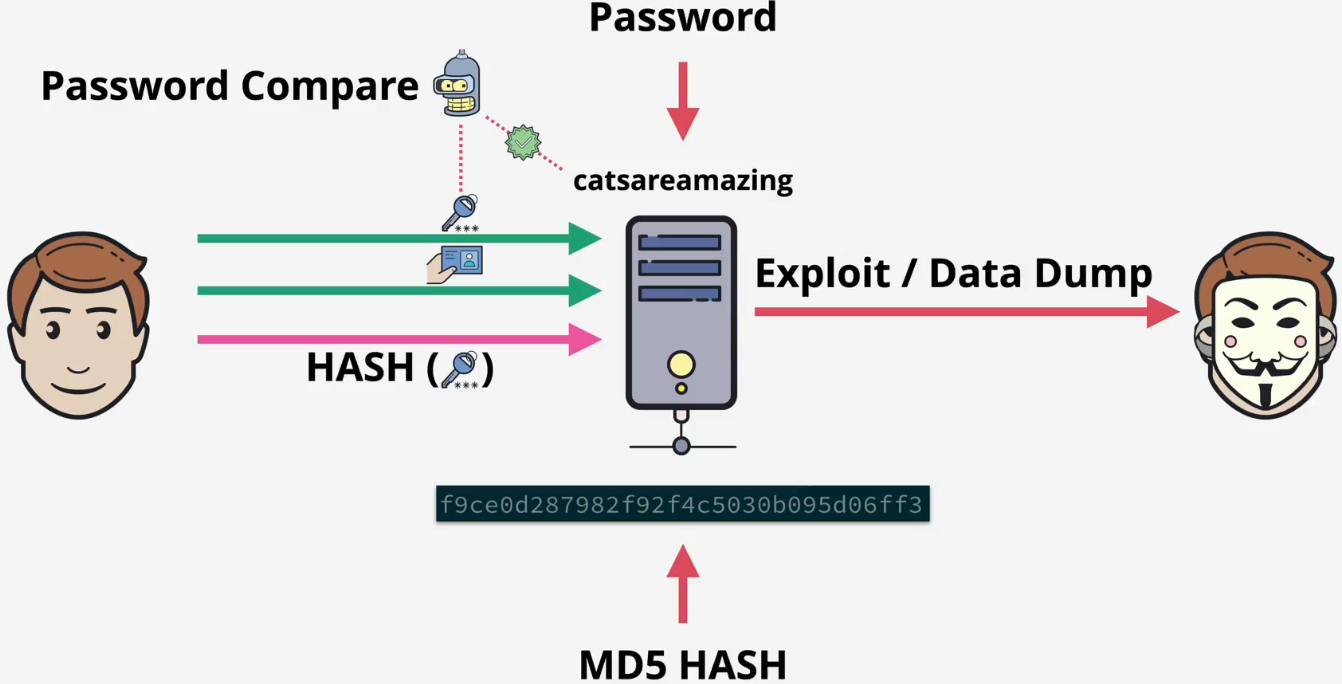
How it works?
- When you create an account
- The server takes your password
- It scrambles it into a unique code called a hash using a special function
- Crucially, it only saves this hash, not your actual password
- When you log in
- You enter the password
- The server takes what you just typed and scrambles it into a new hash using the exact same function
- It then compares the new hash to the hash it has stored
- The result
- If the two hashes match, you are logged in
- If they do not match, access is denied
Weakness - collision

ls
plane.jpg ship.jpg
md5 plane.jpg
MD5 (plane.jpg) = 253dd04e87492e4fc3471de5e776bc3d
md5 plane.jpg
MD5 (plane.jpg) = 253dd04e87492e4fc3471de5e776bc3d
md5 ship.jpg
MD5 (ship.jpg) = 253dd04e87492e4fc3471de5e776bc3d
shasum -a 256 plane.jpg
91e34644af1e6c36166e1a69d915d8ed5dbb43ffd62435e70059bc76a742daa6 plane.jpg
shasum -a 256 ship.jpg
caf110e4aebe1fe7acef6da946a2bac9d51edcd47a987e311599c7c1c92e3abd ship.jpg