complexity
Time Complexity
Time complexity is defined as the amount of time taken by an algorithm to run, as a function of the length of the input
Example
def sum(arr):
sum = 0
for x in arr:
sum = sum + x
return sum
The time complexity = O(n)
Common Types
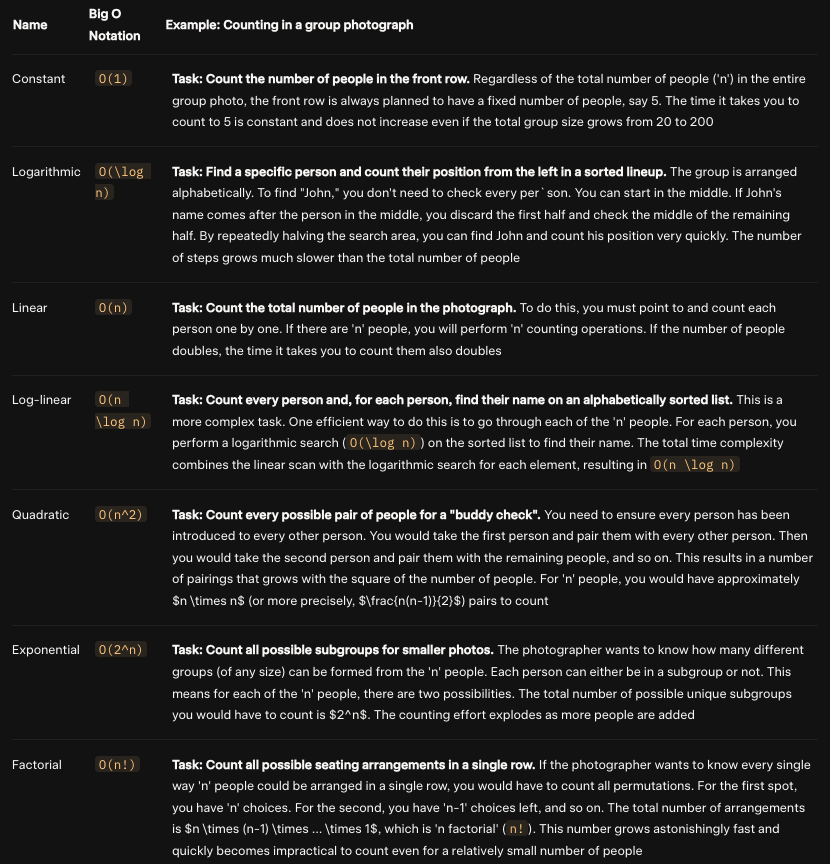
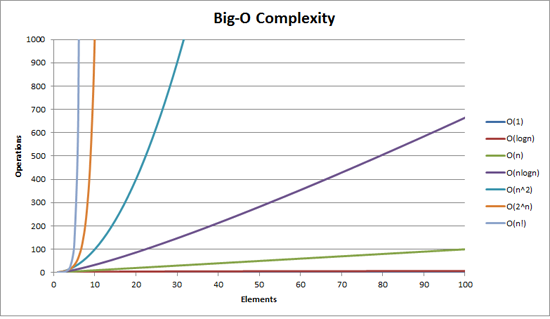
Common Sorts
| Algorithm | Best Case Time Complexity | Average Case Time Complexity | Worst Case Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Search | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Binary Search | O(1) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Bubble Sort | O(n) | O(n²) | O(n²) |
| Selection Sort | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(n²) |
| Insertion Sort | O(n) | O(n²) | O(n²) |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Quick Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n²) |
| Heap Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Bucket Sort | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | O(n²) |
| Radix Sort | O(nk) | O(nk) | O(nk) |
| Tim Sort | O(n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
| Shell Sort | O(n) | O((n log n)²) | O(n²) |
Space Complexity
Space complexity refers to the total amount of memory space used by an algorithm/program, including the space of input values for execution
In the interview, we rarely count the space of input values. However, we're better ask the interviewer.
Example
def sum(arr):
sum = 0
for x in arr:
sum = sum + x
return sum
The space complexity = O(1) ~ constant