iam
Basics
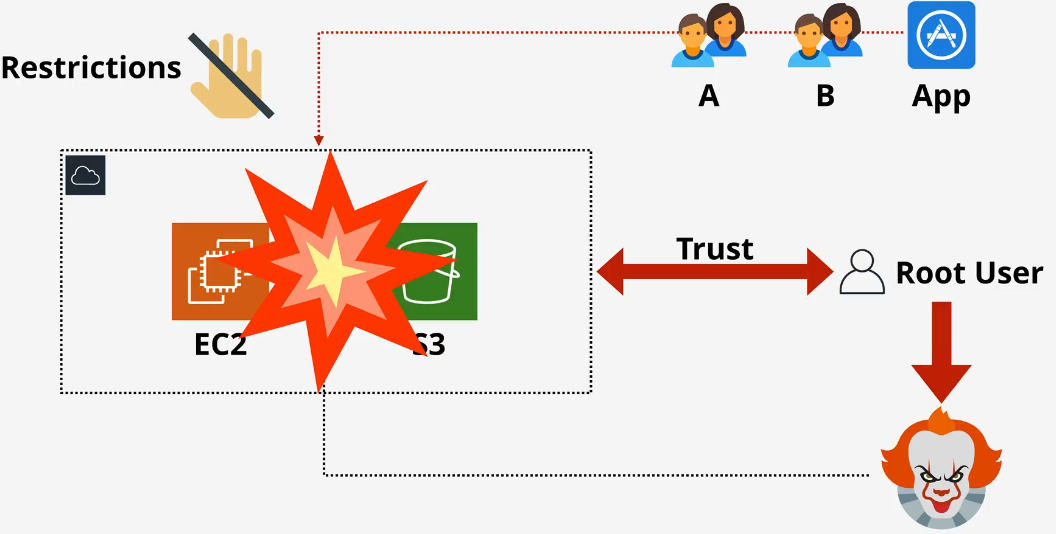
Problem
Solution
- IAM has the same level of permissions and authorization as the root user in the account

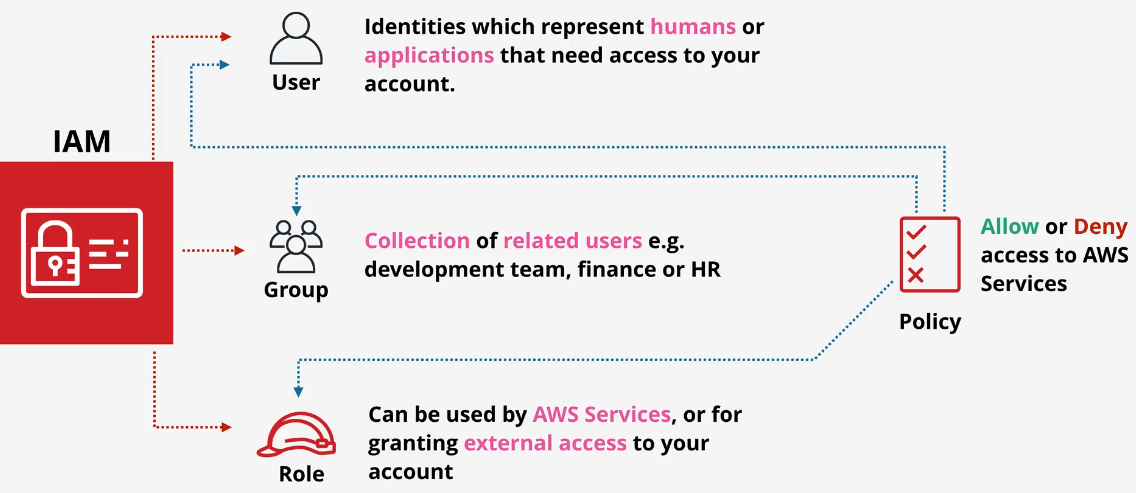
Three main jobs
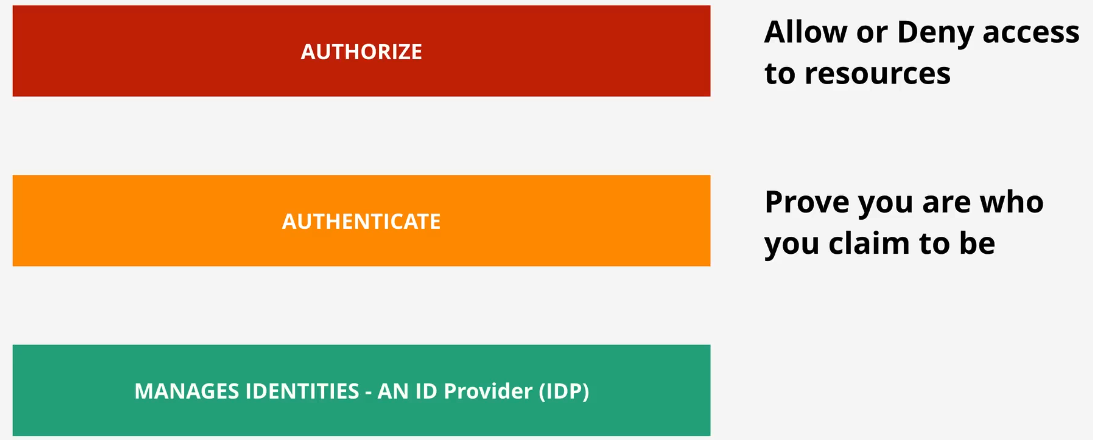
Key features
- No cost
- Global service/Global resilience
- Allow or deny its identities on its AWS account
- No direct control on external accounts or users
- Identity federation and MFA
- Use Facebook, Twitter, Google, etc. to access AWS resources
Access Keys
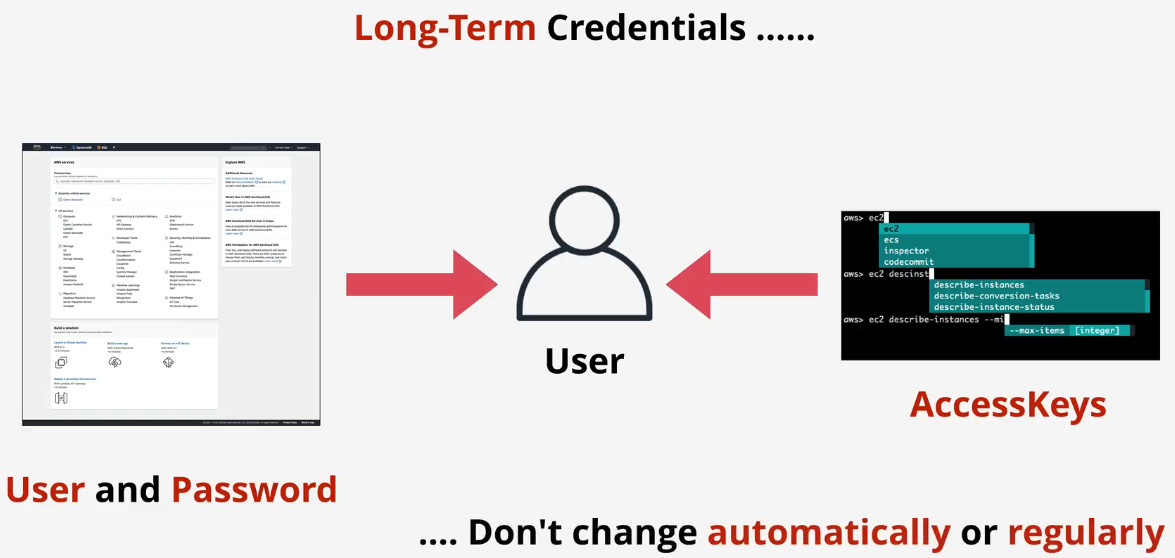
Key features
- An IAM user has 1 username and 1 password
- An IAM user can have two access keys
- Access keys are provided during initialization and are used to access the AWS CLI
- Access keys can be created, deleted, made inactive, or made active
- They should be deleted and recreated if they are leaked
- Access keys consists of two parts
- Access Key ID: ABABABABABABABA
- Secret Access Key: oWerWRhoefWO/RIOF/DFLWAnljef
Demo
General Account
Root account
- Account alias
- Used for sign-in URL
- Create → Fill in "Preferred alias"
- Users
- User → Add users
- Username
- Credential type
- Set permissions
- User → Add users
IAM account
- Login
- Account ID or account alias
- IAM user name
- Password
- Setup MFA
Production Account
Same to general account
Access Key and AWS CLI
Access key
- IAM accounts (General and Production)
- Create access key → Download .csv file
AWS CLI
- Installing, updating, and uninstalling the AWS CLI version 2
- Using profile for working with multiple accounts, regions, or roles
aws configure --profile <profile_name>
---
AWS Access Key ID [None]:
AWS Secret Access Key [None]:
Default region name [None]:
Default output format [None]:
aws s3 ls --profile <profile_name>