cloud computing
Definition
NIST - 5 characteristics
- On-demand self-service
- Can provision capabilities as needed without requiring human interaction
- Provision and terminate using a UI/CLI without human interaction
- Broad network access
- Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms
- Access services over any networks, on any devices, using standard protocols and methods
- Resource pooling
- There is a sense of location independence, no control or knowledge over the exact location of the resources
- Resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model
- Economies of scale, cheaper service
- Rapid elasticity
- Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released to scale rapidly outward and inward with demand
- To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited
- Scale up (out) and down (in) automatically in response to system load
- Measured service
- Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, reported, and billed
- Usage is measured. Pay for what you consume
Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid vs. Multi Cloud
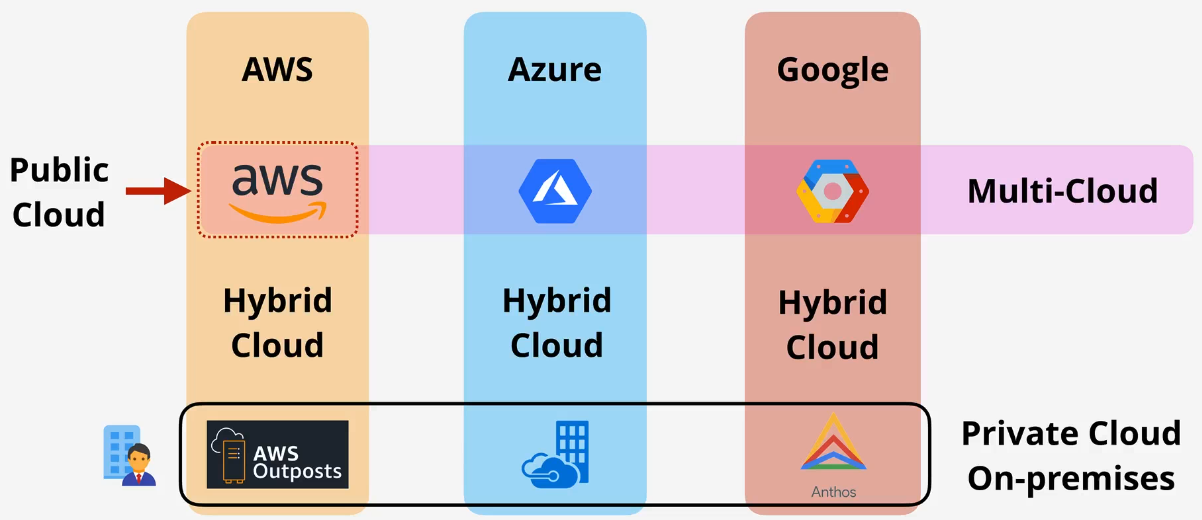
Public cloud
- Using 1 public cloud
Private cloud
- Using an on-premises real cloud
Multi-cloud
- Using more than 1 public cloud
Hybrid cloud
- Using both public and private clouds
- Not public cloud + legacy on-premises
note
Public cloud and private cloud must meet the 5 essential characteristics of cloud computing
Cloud Service Models
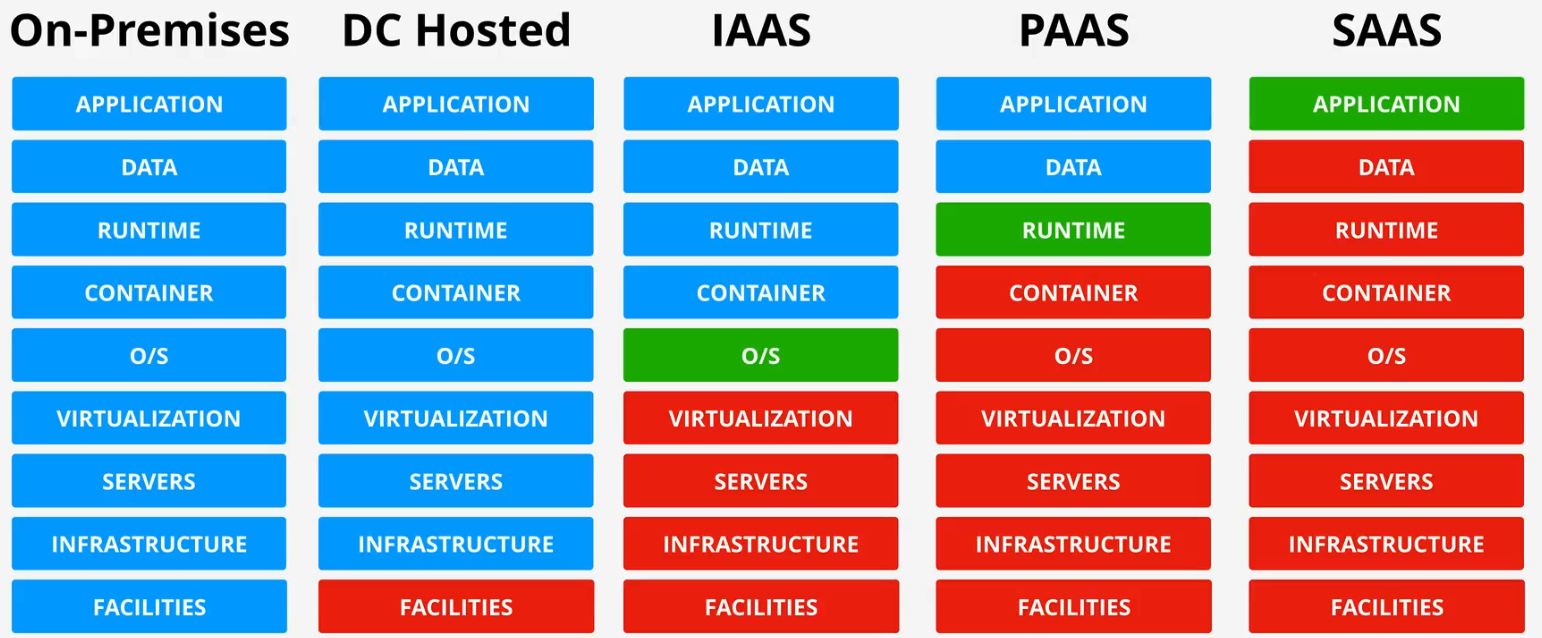
- Blue: Managed by the user
- Red: Managed by the vendor
- Green: Unit of consumption
Terms and concepts
- Infrastructure stack
- Parts you manage
- Parts managed by the vendor
- Unit of consumption
Stacks layers
- Facilities: Building, physical security, power, air conditioner, staffing
- Infrastructure: Storage, networking, compute resources
- Servers: Physical hardware
- Virtualization: Servers run virtualization software, such as VMware, Hyper-V, etc.
- Operating system: Virtual machines run an operating system (OS)
- Container: The OS runs containers, such as Docker, etc.
- Runtime: The environment (e.g., Python, Java, etc.) required for the application to run
- Data: Data required to run the application
- Application: The software or application itself