assess vault token
The token is retained in its original form for display but is invalid
Token Update for Vault 1.10
Vault 1.10 introduced significant token changes
- Token prefixes updated
- Service tokens: hvs.xxx (previously s.xxx)
- Batch tokens: hvb.xxx (previously b.xxx)
- Recovery tokens: hvr.xxx (previously r.xxx)
- Service tokens now require a minimum length of 95 bytes
Intro to Vault Tokens
Vault interfaces
- Token generation
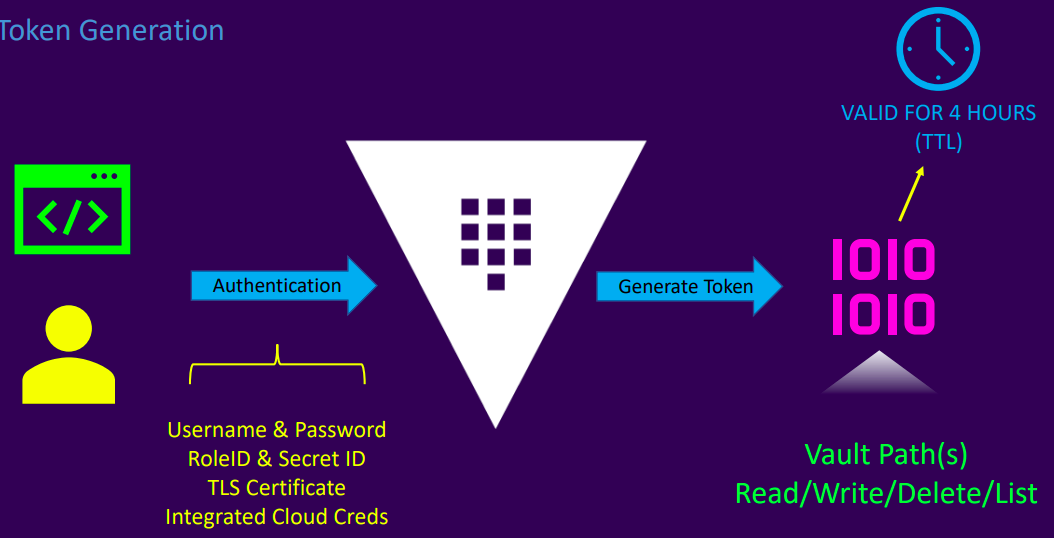
- Token usage
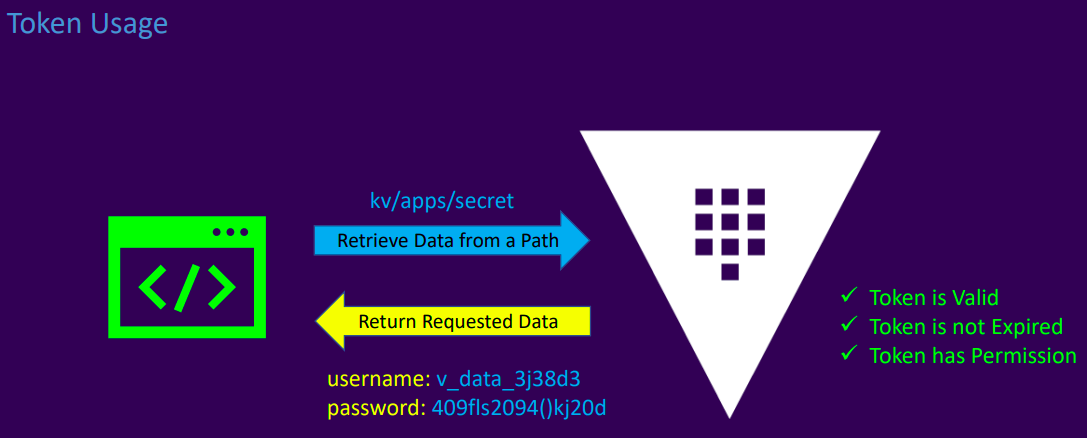
Key features
- Tokens are the primary authentication method in Vault
- Most operations require a token, except for login paths
- The token auth method, which cannot be disabled, manages token creation and storage
- Tokens can be used directly or with other auth methods (e.g., LDAP) to dynamically generate tokens
- Policies attached to tokens define their permissions
Token types
- Service tokens (Default)
- Persisted to storage, involving heavy read/write operations
- Features: Renewable, revocable, and capable of creating child tokens
- Commonly used in Vault operations
- Example: hvs.xxx
- Batch tokens
- Lightweight, encrypted blobs not persisted to storage
- Ideal for high-volume tasks (e.g., encryption, DR replication)
- Limited features compared to service tokens
- Example: hvb.xxx
Comparing token types
| Characteristic | Service Tokens | Batch Tokens |
|---|---|---|
| Can be root tokens | Yes | No |
| Can create child tokens | Yes | No |
| Renewable | Yes | No |
| Can be periodic | Yes | No |
| Can have explicit Max TTL | Yes | No |
| Has an accessor | Yes | No |
| Has Cubbyhole | Yes | No |
| Revoked with parent (if not orphan) | Yes | Stops working |
| Dynamic secrets lease assignment | Self | Parent (if not orphan) |
| Can be used across performance replication clusters | No | Yes |
| Creation scales with performance standby node count | No | Yes |
| Performance cost | Heavyweight (Multiple writes per token creation) | Lightweight (No storage cost for token creation) |
Tokens include metadata such as
- Accessor
- Policies
- TTL/Max TTL
- Number of uses left
- Orphan token
- Renewal status
Example token lookup
vault token lookup hvs.d1BCdhug8buTgAnSZhtPm8Hp
---
Key Value
--- -----
accessor 5mXJQjjQvG44ymJZ0lSHihTG
creation_time 1630436317
creation_ttl 768h
display_name token
entity_id n/a
expire_time 2021-10-02T14:58:37.2194177-04:00
explicit_max_ttl 0s
id hvs.d1BCdhug8buTgAnSZhtPm8Hp
issue_time 2021-08-31T14:58:37.2194177-04:00
meta <nil>
num_uses 0
orphan false
path auth/token/create
policies [default user]
renewable true
ttl 767h59m47s
type service
Token Hierarchy
Key features
- Each token has a time-to-live (TTL), except root tokens, which have no TTL
- Tokens are revoked upon reaching their TTL unless renewed
- Tokens reaching their maximum TTL are revoked
- Tokens can be manually revoked early
- Revoking a parent token revokes all its child tokens
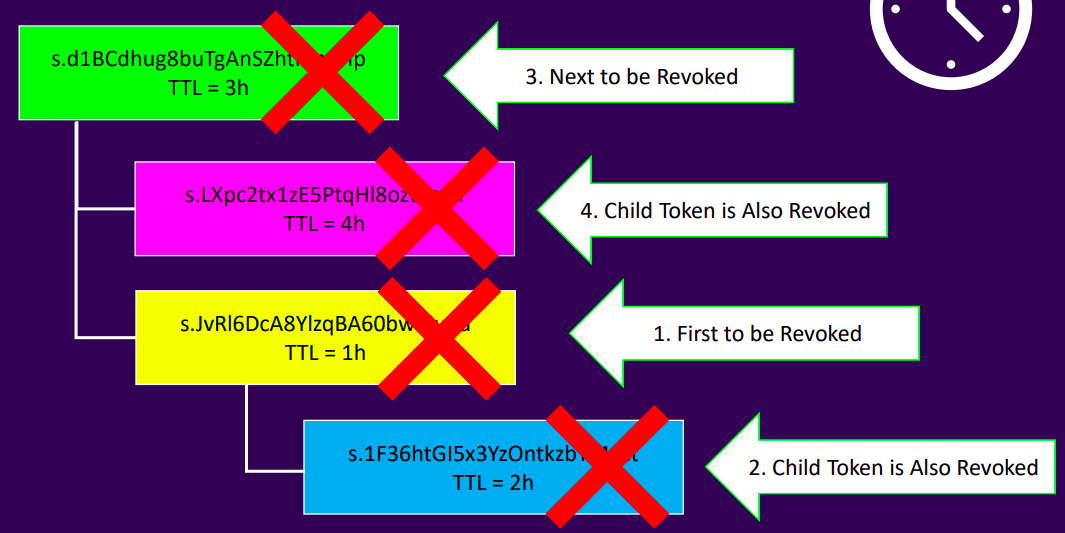
Controlling the Token Lifecycle
Behaviors
- App Developer: "My long-running app can't regenerate tokens or secrets"
- Solution: Use a periodic service token
- Principal Engineer: "I need a token that auto-revokes after one use"
- Solution: Use a service token with a use limit
- DevOps: "My app can't use a token influenced by its parent's expiration"
- Solution: Use an orphan token
Summary
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Long-running app unable to regenerate tokens/secrets | Periodic Service Token |
| Token must revoke after one use | Service Token with Use Limit |
| Token expiration must not depend on parent | Orphan Service Token |
Periodic Tokens
Key features
- Ideal when token revocation is problematic
- Root or sudo users can generate periodic tokens
- Periodic tokens have a TTL but no maximum TTL
- They can persist indefinitely if renewed within their TTL
- Useful for long-running services unable to regenerate tokens
This is particularly effective for applications requiring continuous operation without token regeneration
Policy example
path "auth/token/create" {
capabilities = ["create", "read", "update", "delete", "sudo"]
}
Token creation (No max TTL)
- period → token_duration
vault token create -policy=training -period=24h
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
token_accessor 73rjN1kmnzwT71pMw9H7p6P9
token_duration 24h
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
identity_policies []
policies ["default", "training"]
Token lookup
vault token lookup hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
---
Key Value
--- -----
accessor 73rjN1kmnzwT71pMw9H7p6P9
creation_time 1632751059
creation_ttl 24h
display_name token
entity_id n/a
expire_time 2021-09-28T09:57:39.7239753-04:00
explicit_max_ttl 0s # Does not have max TTL
id hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
issue_time 2021-09-27T09:57:39.7239753-04:00
meta <nil>
num_uses 0
orphan false
path auth/token/create
period 24h
policies ["default", "training"]
renewable true
ttl 23h59m28s
type service
Service Tokens With Use Limits
Key features
- Limits the number of requests a token can make to Vault
- Use limits complement TTL and Max TTL
- Tokens expire after their last use, regardless of remaining TTL
- Tokens expire at TTL's end, regardless of remaining uses
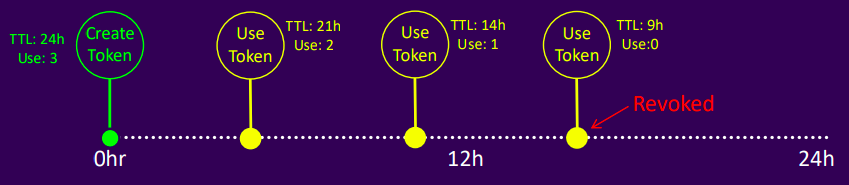
Example
vault token create -policy="training" -use-limit=2
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.516LO9Ssk1CQzvKo8ny1G0eu
vault token lookup hvs.516LO9Ssk1CQzvKo8ny1G0eu
---
Key Value
--- -----
id hvs.516LO9Ssk1CQzvKo8ny1G0eu
issue_time 2021-12-25T18:35:08.004652-08:00
meta <nil>
num_uses 2
Orphan Tokens
Key features
- Ideal when default token hierarchy behavior is undesirable
- Root or sudo users can create orphan tokens
- Orphan tokens are not children of their parent
- Orphan tokens are independent of their parent and don't expire with it
- They expire only when their own Max TTL is reached
Policy example
path "auth/token/create-orphan" {
capabilities = ["create", "read", "update", "delete", "sudo"]
}
Example
---
vault token create -policy="training" -orphan
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.3rPJCQbGWD9O6uybtTuojjFs
vault token lookup hvs.3rPJCQbGWD9O6uybtTuojjFs
---
Key Value
--- -----
id hvs.3rPJCQbGWD9O6uybtTuojjFs
issue_time 2018-12-13T18:35:41.02532-08:00
meta <nil>
num_uses 0
orphan true
Setting the Token Type
Periodic token example
vault token create -policy="training" -period="24h"
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
token_accessor 73rjN1kmnzwT71pMw9H7p6P9
token_duration 24h
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
identity_policies []
policies ["default", "training"]
Batch token configuration (AppRole)
vault auth enable approle
vault write auth/approle/role/training policies="training" \
token_type="batch" \
token_ttl="60s"
Periodic token configuration (AppRole)
vault write auth/approle/role/jenkins policies="jenkins" \
period="72h"
Managing Tokens Using CLI
Use the vault token command
- capabilities
- create
- lookup
- renew
- revoke
Use command
- Syntax:
vault <object_type> <subcommand> <policy> <validity_length>
Examples
- Create a token
vault token create -ttl=5m -policy=training
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.12VNpg4OA9tTdCd4V6ODuDRK
token_accessor lMIaZ4Tn1t57wKXdsfNv7vlm
token_duration 5m
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
identity_policies []
policies ["default", "training"]
- Create a token with multiple policies
vault token create \
-display_name=jenkins \
-policy=training,certs \
-ttl=24h \
-explicit-max-ttl=72h
- Lookup token information
vault token lookup hvs.12VNpg4OA9tTdCd4V6ODuDRK
---
Key Value
--- -----
accessor lMIaZ4Tn1t57wKXdsfNv7vlm
creation_time 1630613718
creation_ttl 5m
display_name token
entity_id n/a
expire_time 2021-09-02T16:23:02.6427677-04:00
explicit_max_ttl 0s
id hvs.12VNpg4OA9tTdCd4V6ODuDRK
issue_time 2021-09-02T16:15:18.5177235-04:00
last_renewal 2021-09-02T16:18:02.6427677-04:00
last_renewal_time 1630613882
meta <nil>
num_uses 0
orphan false
path auth/token/create
policies ["default", "training"]
renewable true
ttl 3m12s
type service
- Revoke a token
vault token revoke hvs.12VNpg4OA9tTdCd4V6ODuDRK
---
Success! Revoked token (if it existed)
- Check token capabilities
vault token capabilities hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg kv/data/apps/webapp
---
create, list, read, sudo, update
- Renew a token
vault token renew hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg
token_accessor INk5tw0tl3N2xs0XZZfPc9Tq
token_duration 5m
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
identity_policies []
policies ["default", "training"]
Managing Tokens Using UI
Directions: Homepage → Profile → Copy token
Managing Tokens Using API
Key features
- Authentication via an auth method returns a JSON response containing a token
- Parse the response (e.g., using jq) to extract .auth.client_token
- Include the token in future Vault requests via
- X-Vault-Token header, or
- Authorization: Bearer header
Authenticate and parse Token
curl --request POST --data @payload.json http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/userpass/login/kyphan | jq
---
{
"request_id": "0b4181fe-0dec-2261-5231-bb3f033387e5",
"auth": {
"client_token": "hvs.WNS4zL4c4wQJet9KS9KItkHW",
"accessor": "zsap13bBoQGzB5xVPZFEu3Th",
"policies": ["default", "training"],
"token_policies": ["default", "training"],
"metadata": {"username": "kyphan"},
"lease_duration": 2764800,
"renewable": true,
"entity_id": "88669d54-b405-c27a-d468-410a1185eb0d",
"token_type": "service",
"orphan": true
}
}
Store token in a file
curl --request POST --data @payload.json http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/userpass/login/kyphan | jq -r ".auth.client_token" > token.txt
cat token.txt
---
hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg
Store token in an environment variable
OUTPUT=$(curl --request POST --data @payload.json http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/userpass/login/kyphan)
VAULT_TOKEN=$(echo "$OUTPUT" | jq -r '.auth.client_token')
echo "$VAULT_TOKEN"
---
hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg
Use token in requests
- Store a secret
curl --header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg" \
--request POST \
--data '{ "apikey": "3230sc$832d" }' \
https://vault.example.com:8200/v1/secret/apikey/splunk
- Retrieve a secret
curl --header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg" \
--request GET \
https://vault.example.com:8200/v1/secret/data/apikey/splunk
Root Tokens
Key features
- Root tokens are superusers with unlimited Vault access
- They have no TTL (do not expire) and are tied to the root policy
- Root tokens can create other root tokens with a TTL
- Usage: Avoid daily use, revoke after necessary tasks
Initial root token
- Generated during Vault initialization
- Used for initial setup (e.g., auth methods, audit devices)
- Revoke after configuring and testing new auth methods
vault token revoke hvs.dhtIk8VsE3Mj61PuGP3ZfFrg
---
Success! Revoked token (if it existed)
Create root token from existing root token
vault login hvs.lmmOCfNH1HZvvBwxnLErWrhK # Root token
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.lmmOCfNH1HZvvBwxnLErWrhK
token_accessor 5UNwzGSr1TOGymhERwZeAMgr
token_duration ∞
token_renewable false
token_policies ["root"]
policies ["root"]
vault token create
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.tiRn8HflpBJNssFaSWTTCOI2 # New root token
token_accessor anZIDsIUzPUcs6hKKsOdwOXj
token_duration ∞
token_renewable false
token_policies ["root"]
policies ["root"]
Generate root token with unseal/recovery keys
- Useful in emergencies or for specific tasks
- Requires a quorum of unseal key holders to prevent single-person control
Steps
- Initialize root generation
vault operator generate-root -init
---
Nonce 5b6e3831-2a45-4695-7757-5810074d36c8
Started true
Progress 0/1
Complete false
OTP E87jF6ZeJo8NjJwvytl7mvKLEr
OTP Length 26
- Key holders provide unseal keys
vault operator generate-root
Unseal Key (will be hidden):
---
Nonce f8579a51-5138-c319-445d-2d3640119f87
Started true
Progress 1/3
Complete false
- Complete generation
vault operator generate-root
Unseal Key (will be hidden):
---
Nonce f8579a51-5138-c319-445d-2d3640119f87
Started true
Progress 3/3
Complete true
Encoded Token G2NeKUZgXTsYYxILAC9ZFBguPw9ZXBovFAs
- Decode root token
vault operator generate-root \
-otp="hM9q24nNiZfnYIiNvhnGo4UFc3" \
-decode="G2NeKUZgXTsYYxILAC9ZFBguPw9ZXBovFAs"
---
Root token: hvs.gXtT3uq9teYf0ZnFQH6hOiw8
Token Accessors
Key features
- Every token has an associated accessor, a reference used for limited actions
- Look up token properties
- Look up token capabilities
- Renew the token
- Revoke the token
Accessors cannot authenticate to Vault or perform additional requests
Examples
- Root token accessor
vault login hvs.cbC7GJ6U6WJaDuDSgkyVcKDv
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.cbC7GJ6U6WJaDuDSgkyVcKDv
token_accessor K6pHtVc9LbXQdUavg2J1Ixa2
token_duration ∞
token_renewable false
token_policies ["root"]
policies ["root"]
- Regular token accessor
vault token create -policy=training -ttl=30m
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.5YmCHHV80mN3dJpzOwvVAYk8
token_accessor 2ogWa36gDH5wsO8VbuxroByx
token_duration 30m
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
policies ["default", "training"]
Actions with accessors
- View token properties
vault token lookup -accessor gFq2UwnJ0jo87kESKwUcl1Ub
---
Key Value
--- -----
accessor gFq2UwnJ0jo87kESKwUcl1Ub
creation_time 1632576647
creation_ttl 30m
display_name token
entity_id n/a
expire_time 2021-09-25T10:00:47.0615482-04:00
explicit_max_ttl 0s
id n/a
issue_time 2021-09-25T09:30:47.0615482-04:00
meta <nil>
num_uses 0
orphan false
path auth/token/create
policies ["default", "training"]
renewable true
ttl 29m18s
type service
- Revoke a token
vault token create -policy=training -ttl=30m
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.5YmCHHV80mN3dJpzOwvVAYk8
token_accessor 2ogWa36gDH5wsO8VbuxroByx
token_duration 30m
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
policies ["default", "training"]
vault token revoke -accessor 2ogWa36gDH5wsO8VbuxroByx
---
Success! Revoked token (if it existed)
- Renew a token
vault token renew -accessor gFq2UwnJ0jo87kESKwUcl1Ub
---
Key Value
--- -----
token n/a
token_accessor gFq2UwnJ0jo87kESKwUcl1Ub
token_duration 30m
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
policies ["default", "training"]
Limitation of accessors
- Cannot use an accessor to perform traditional Vault actions
vault token create -policy=training -ttl=30m
---
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.vZRfetFFawRIVKJu8Uc50M9o
token_accessor gFq2UwnJ0jo87kESKwUcl1Ub
token_duration 30m
token_renewable true
token_policies ["default", "training"]
policies ["default", "training"]
export VAULT_TOKEN=gFq2UwnJ0jo87kESKwUcl1Ub
vault kv get secret/apps/training
---
Error making API request
URL: GET http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/sys/internal/ui/mounts/secret/apps/training
Code: 403. Errors:
* permission denied
Explaining Time-to-Live (TTL)
Key features
- Every non-root token has a TTL, defining its validity period from creation or renewal
- Example: A new token with a 30-minute TTL is valid for 30 minutes from creation
- Example: A renewed token gets a fresh 30-minute TTL
- When TTL expires, the token is revoked and becomes invalid for authentication. Renewal must occur before expiration
- Tokens may also have a Max TTL, limiting renewals; once reached, the token cannot be renewed further
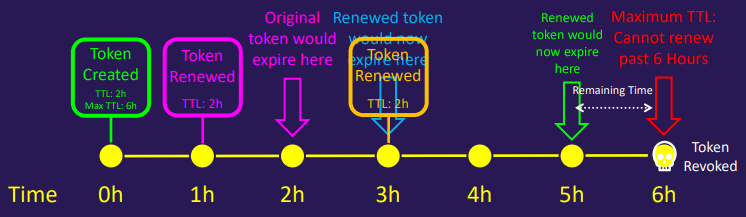
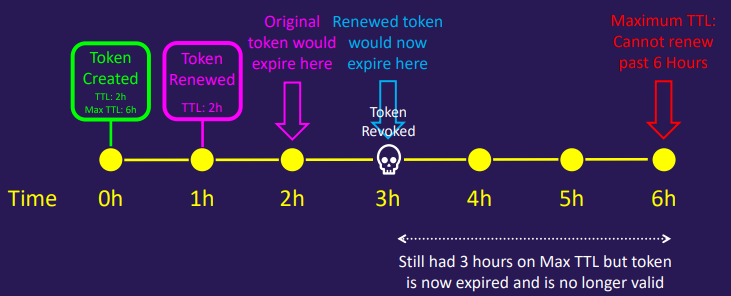
A token can have a TTL and a Max TTL
- The token can be renewed up until the Max TTL
- Once the token hits the Max TTL, it cannot be renewed further
Example
Default TTL
- Vault's default TTL is 768 hours (32 days), adjustable via the configuration file
default_lease_ttl = 24h
Setting TTL
- Explicitly set TTL during creation
vault token create -policy=training -ttl=60m
- Configure auth method for specific TTL
vault write auth/approle/role/training-role \
token_ttl=1h \
token_max_ttl=24h
- Default TTL applied if unspecified, Vault applies the default TTL
vault token create -policy=training
Create a Token Based on Use Cases
Long-running application
- Needs: App cannot regenerate tokens/secrets; token renewable indefinitely
- Solution: Periodic token
Limited use
- Needs: Token usable only 3 times, regardless of TTL
- Solution: Service token with use limits
Independent lifecycle
- Needs: Token unaffected by parent's lifecycle, with extended expiration
- Solution: Orphan token
CIDR
- Needs: Token used by a specific host or within a certain network block
- Solution: CIDR-bound token
Replication and efficiency
- Needs: Token replicated across clusters, minimal storage overhead for mass creation
- Solution: Batch token