compare and configure secret engines - pending
Static vs. Dynamic Secrets
Challenges with static secrets
- Expiration: Never expire, often required by legacy apps
- Security: Shared among team members, lacking accountability
- Validity: Always active, making them prime targets for attackers
- Rotation: Rarely rotated, manual process
- Longevity: Persist indefinitely due to technical debt or turnover
Benefits of dynamic secrets
- On-Demand Creation: Generate secrets as needed
- Debt Reduction: Secrets are revoked in Vault and at the source
- Leases: Each secret has a lease for lifecycle management
- Renewal: Fine-grained control over renewability
- Expiration: Leases define validity periods
- Revocation: Auto-expire or manually revoke secrets
Examples
- Application using Vault
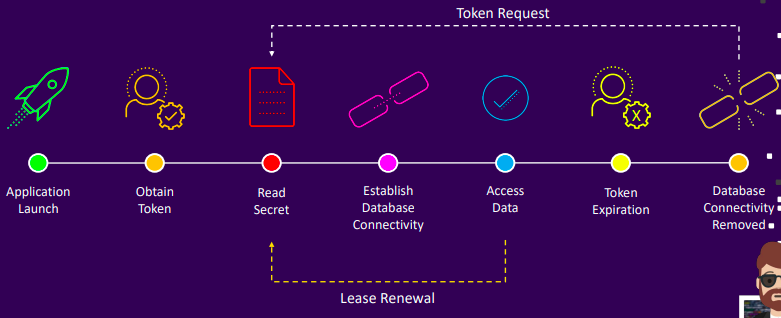
- Pipeline using Vault
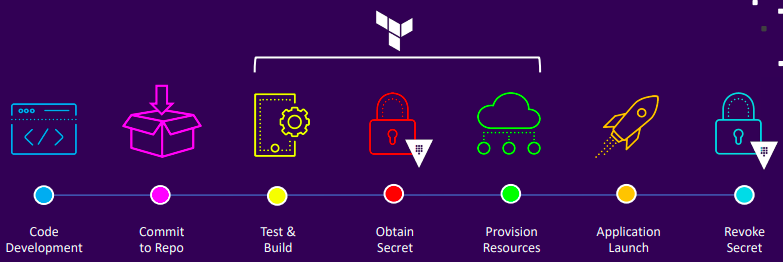
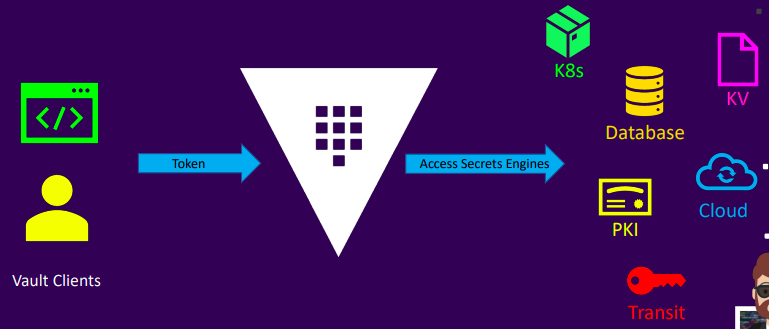
Intro to Secrets Engines
Key features
- Secrets engines store, generate, or encrypt data as plugins in Vault
- Multiple engines, including duplicates, can be enabled at unique paths
- Interaction occurs via the engine's designated path
What is a secret?
- Sensitive data, such as
- Username/password
- TLS certificates
- API keys
- Database credentials
- Application data
- Any plaintext-sensitive information
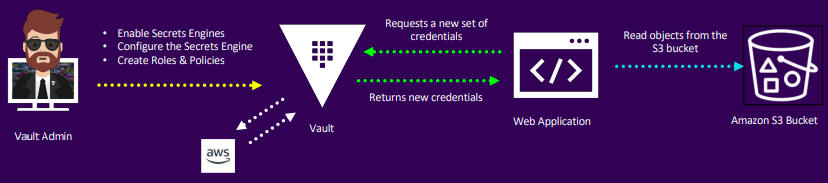
Secrets as a service
- Vault generates and manages credentials on-demand
- Eliminates credential sharing with automatic revocation at lease end
- Provides audit trails and role-based access via policies
Example
Types of secrets engines
- By category
- Cloud: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Google Cloud KMS, Alibaba Cloud
- Databases: Cassandra, InfluxDB, MongoDB, MSSQL, MySQL/MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SAP HANA, Snowflake
- Other: Active Directory, Consul, Cubbyhole, KV, Key Management, Identity, RabbitMQ, Nomad, SSH, TOTP, Terraform Cloud, KMIP, PKI, Transform, Transit, Venafi
- Specific engines
- KV: Key/Value (v1: non-versioned; v2: versioned)
- Database: Supports Cassandra, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, etc.
- Key Management: Integrates with Azure Key Vault, AWS KMS, GCP Cloud KMS
Secrets engine Functions
| Engine | Function |
|---|---|
| Active Directory | Rotates existing AD account passwords based on thresholds. |
| AliCloud | Generates access tokens or STS credentials based on RAM policies/roles. |
| AWS | Creates IAM-based AWS credentials, STS credentials, or federation tokens. |
| Azure | Generates Azure service principals with role/group assignments. |
| Consul | Produces Consul API tokens based on ACL policies. |
| Cubbyhole | Stores sensitive data tied to a token; expires with the token; inaccessible to other tokens. |
| Database | Generates dynamic credentials for various databases using custom statements. |
| Google Cloud | Creates service account keys and OAuth tokens based on IAM policies. |
| Google Cloud KMS | Offers encryption and key management via Google Cloud KMS. |
| Key Management | Manages cryptographic keys across KMS providers. |
| KMIP | Acts as a KMIP server, managing object lifecycles. |
| KV | Stores key/value pairs (v1: unversioned; v2: versioned). |
| Identity | Default identity management for Vault; cannot be disabled or re-enabled. |
| MongoDB Atlas | Generates API keys for MongoDB Atlas projects/organizations with specific roles. |
| Nomad | Creates Nomad ACL tokens based on existing policies. |
| OpenLDAP | Manages LDAP passwords and creates dynamic credentials. |
| PKI | Issues x.509 certificates, acting as a root or intermediate CA. |
| RabbitMQ | Generates user credentials based on permissions and virtual hosts. |
| SSH | Enables secure SSH authentication and authorization. |
| Terraform Cloud | Produces Terraform Cloud API tokens for organizations, teams, and users. |
| TOTP | Generates time-based one-time passwords per the TOTP standard. |
| Transform | Transforms and tokenizes data securely. |
| Transit | Provides encryption-as-a-service for data in transit. |
| Venafi | Issues SSL/TLS certificates via Venafi Trust Protection Platform or Venafi Cloud for machine identities. |
Working With a Secrets Engine
Key features
- Default Engines: Cubbyhole and Identity are enabled by default and cannot be disabled
- Enabling Engines: Other engines must be explicitly enabled via CLI, API, or UI (for most)
- Path Isolation: Engines are enabled at unique, meaningful paths for interaction
Responsibilities
- Privileged users (e.g., Vault Admins)
- Enable secrets engines
- Configure backend platform connections (e.g., AWS, databases)
- Define roles for backend permissions
- Create policies for secrets engine access
- Vault clients (e.g., users, apps)
- Retrieve credentials using tokens and policies
- Renew leases or tokens as needed, if permitted
CLI
-
Use the vault secrets command
- disable
- enable
- list
- move
- tune
-
Examples
vault secrets enable aws
---
Success! Enabled the aws secrets engine at: aws/
vault secrets tune -default-lease-ttl=72h pki/
- Useful flags
vault secrets list --detailed
vault secrets enable --path=developers kv
vault secrets enable --description="my first kv" kv
vault secrets enable -description="Static Secrets" -path="cloud-kv" kv-v2
- List enabled engines
vault secrets list
---
Path Type Accessor Description
---- ---- -------- -----------
aws/ aws aws_dafa7adc n/a
azure/ aws aws_1a214ff6 n/a
kyphan/ kv kv_28b1ceaa n/a
cloud-team-kv/ kv kv_fa270a3f n/a
cubbyhole/ cubbyhole cubbyhole_88c8e2e3 per-token private secret storage
dev-team-kv/ kv kv_55c319c4 n/a
identity/ identity identity_e60e93cb identity store
kv-v2/ kv kv_eea3206c n/a
sys/ system system_66b0d8ee system endpoints
transit/ transit transit_7b8038ca n/a
UI
- Directions: Homepage → Secrets → Enable new engine
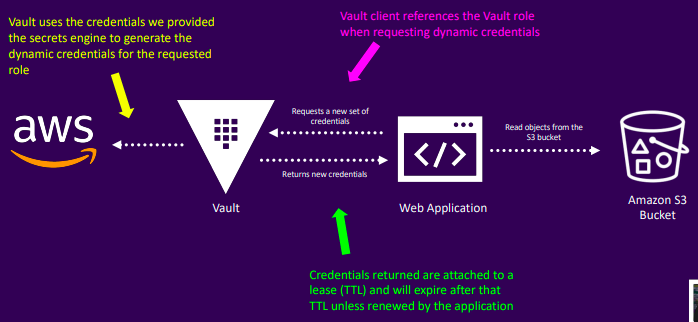
Configuring a Secrets Engine for Dynamic Credentials
Steps
- Step 1: Configure Platform Access - grant Vault permissions to manage credentials on the target platform
- Step 2: Define Roles - set permissions for credential generation
AWS Example
- Step 1: Configure access
vault write aws/config/root \
access_key=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE \
secret_key=wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY \
region=us-east-1
---
Success! Data written to: aws/config/root
- Step 2: Configure roles
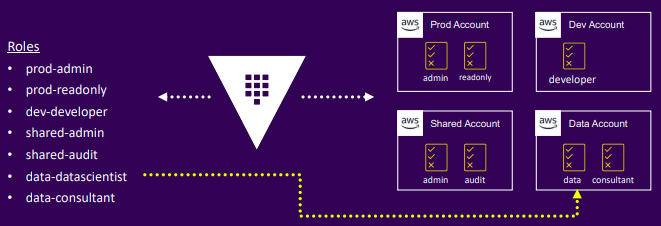
- Generate credentials
vault read aws/creds/data-consultant
---
Key Value
--- -----
lease aws/creds/data-consultant/349dm20s4xp2
lease_duration 24h
lease_renewable true
access_key AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
secret_key wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
security_token <nil>
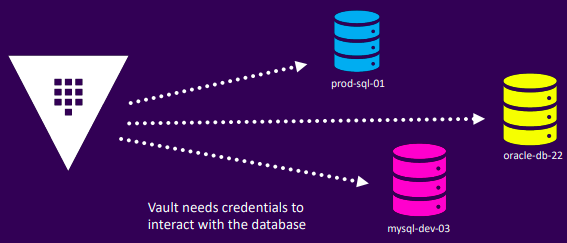
Database Example
- Step 1: Configure access
vault write database/config/prod-database \
plugin_name=mysql-aurora-database-plugin \
connection_url="{{username}}:{{password}}@tcp(prod.cluster.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:3306)/" \
allowed_roles="app-integration, app-lambda" \
username="vault-admin" \
password="vneJ4908fkd3084Bmrk39fmslslf#e&349"
- Step 2: Configure roles
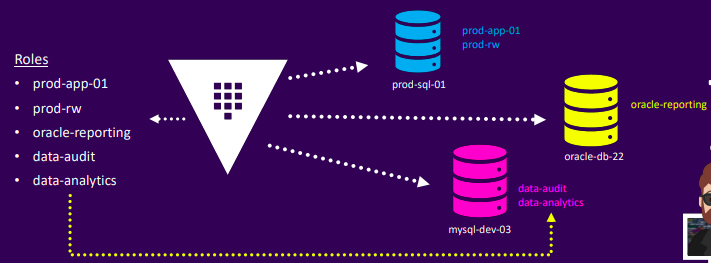
- Generate credentials
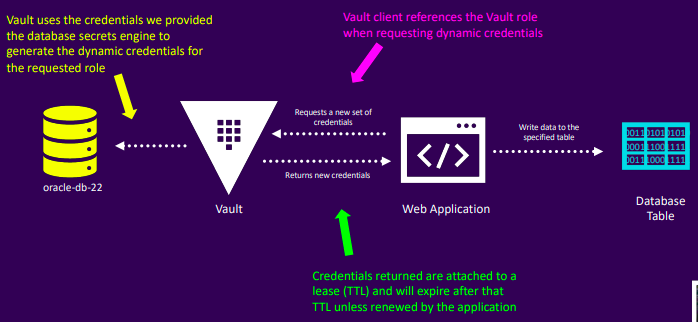
vault read database/creds/oracle-reporting
---
Key Value
--- -----
lease_id database/creds/my-role/2f14c-4aa224b9-ad944a8d4de6
lease_duration 1h
lease_renewable true
password yRUSyd-vPYDg5NkU9kDg
username V_VAULTUSE_MY_ROLE_SJJUK3Q8W3BKAYAN8S62_1602543009
Key/Value Secrets Engine
Key features
- Stores static secrets with two versions: KV v1 (unversioned) and KV v2 (versioned)
- Accessible via UI, CLI, and API; supports interactive or automated use
- Secured with 256-bit AES encryption and policy-based access control (ACLs)
- Frequently used; can be enabled at multiple unique paths
- Stores key-value pairs (e.g., secret/applications/web01)
- Creating a secret requires create capability
- Updating a secret requires update capability; new secrets overwrite old values
- In -dev mode, Vault enables KV v2 at secret/ by default
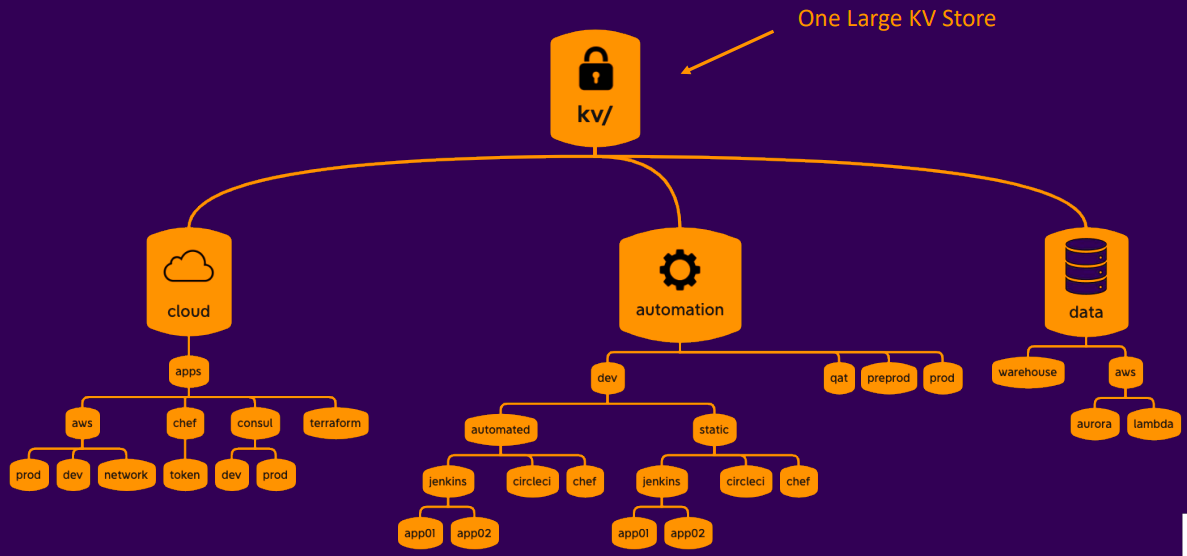
Data Organization
- One large KV store
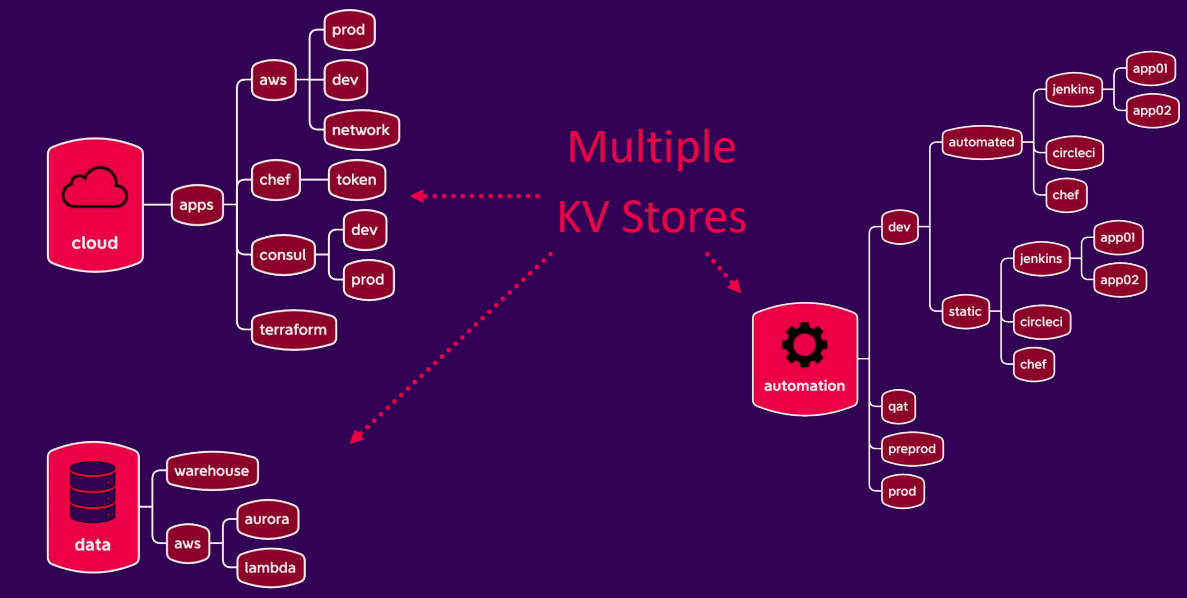
- Multiple KV stores
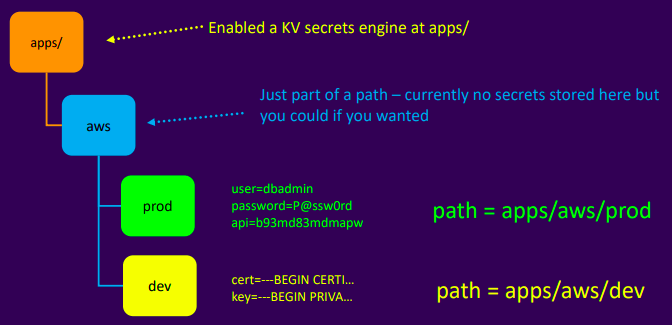
- Paths in KV store
- Flexible storage
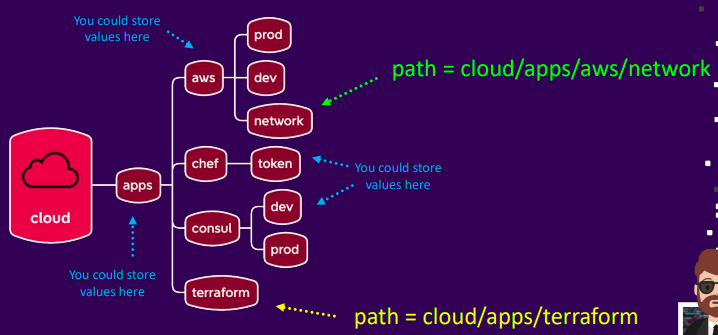
Enabling the Engine
- KV v1
vault secrets enable kv
---
Success! Enabled the kv secrets engine at: kv/
vault secrets enable -path=training kv
---
Success! Enabled the kv secrets engine at: training/
- KV v2
vault secrets enable kv-v2
---
Success! Enabled the kv-v2 secrets engine at: kv-v2/
vault secrets enable -path=training -version=2 kv
---
Success! Enabled the kv-v2 secrets engine at: training/
- List engines
vault secrets list -detailed
---
Path Plugin Accessor Options
---- ------ -------- -------
cubbyhole/ cubbyhole cubbyhole_ee5ae49 map[]
kv/ kv kv_e8b99a3 map[]
training/ kv kv_1d5e9cc1 map[version:2]
Upgrading KV v1 to KV v2
- Irreversible upgrade from v1 to v2; v2-to-v1 downgrade not possible
vault kv enable-versioning training/
---
Success! Tuned the secrets engine at: training/
KV v2 differences
- Metadata: Tracks creation date, version, etc.
- Prefixes
- data/: Stores actual key-value data
- metadata/: Stores secret metadata
- Operational note
- data/ and metadata/ prefixes are required for API and policies
- CLI interactions remain unchanged
- Versioning example
- Write secret (v1): pass=456, api=mfid02s, user=admin
- Update (v2): Overwrites v1
- Delete (v2): Marks as deleted
- Rollback (v3): Restores previous version
- Undelete (v3): Recovers with updates (e.g., pass=789, api=ckj983md)
- Update (v4): New version
- Destroy (v4): Permanently removes a version
- Update (v5, v6): Continues versioning
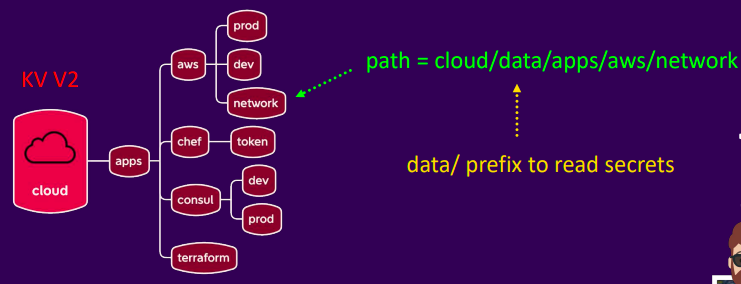
Working With KV Secrets Engine
Use the vault kv command
- put: Write data
- get: Read data
- delete: Remove data
- list: List paths
- undelete: Restore a version (KV v2 only)
- destroy: Permanently delete (KV v2 only)
- patch: Update specific keys (KV v2 only)
- rollback: Revert to a prior version (KV v2 only)
Writing Data
- KV v1 vsKV v2
- Command: Identical for both versions
- Behavior: KV v1 overwrites without versioning; KV v2 tracks versions
# KV v1
vault kv put kv/app/db pass=123
---
Success! Data written to: kv/app/db
# KV v2
vault kv put kv/app/db pass=123
---
Key Value
--- -----
creation_time 2022-12-15T04:35:56.395821Z
deletion_time n/a
destroyed false
version 1
- Multiple key/value pairs
vault kv put kv/app/db pass=123 user=admin api=a8ee4b50cce124
---
Success! Data written to: kv/app/db
- From JSON file
vault kv put kv/app/db @secrets.json
---
Success! Data written to: kv/app/db
- Key notes
- Writing replaces the existing secret (no merge)
# Example
vault kv get kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
pass 123
user admin
api a8ee4b50cce124
# Overwrite
vault kv put kv/app/db api=39cms1204mfi2m
---
Key Value
--- -----
created_time 2022-12-21T14:40:26.886255Z
version 2
# Result
vault kv get kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
api 39cms1204mfi2m
- Recover data (KV v2)
# Rollback to previous version
vault kv rollback -version=1 kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
created_time 2022-12-21T14:49:23.746331Z
version 3
# Restored
vault kv get kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
pass 123
user admin
api a8ee4b50cce124
- Patch Data (KV v2)
# Update specific keys
vault kv patch kv/app/db user=kyphan
---
Key Value
--- -----
created_time 2022-12-22T17:57:35.157363Z
version 4
# Result
vault kv get kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
pass 123
user kyphan
api a8ee4b50cce124
Reading data
- KV v1 vsKV v2
# KV v1 - Returns data only
vault kv get kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
pass 123
user admin
api a8ee4b50cce124
# KV v2 - Includes metadata
vault kv get kv/app/db
---
Key Value
--- -----
creation_time 2022-12-15T04:35:56.395821Z
deletion_time n/a
destroyed false
version 1
pass 123
user admin
api a8ee4b50cce124
- JSON output
vault kv get -format=json kv/app/db
---
{
"request_id": "249fca06-a8ce-5617-d598-1c12384d4ac8",
"data": {
"data": {
"pass": "123",
"user": "admin",
"api": "a8ee4b50cce124"
},
"metadata": {
"created_time": "2022-12-21T13:59:29.917893Z",
"deletion_time": "",
"destroyed": false,
"version": 1
}
}
}
- Key notes
- Reads return the latest version by default
- For deleted secrets (KV v2), only metadata is returned
- Access previous versions with -version=x
vault kv get -version=3 kv/app/db
Deleting data
- KV v1 vsKV v2
# KV v1 - Permanent deletion
vault kv delete secret/app/database
---
Success! Data deleted (if it existed) at: secret/app/database
vault kv get secret/app/database
---
No value found at secret/app/database
# KV v2 - soft deletion (recoverable)
vault kv delete secret/app/web
---
Success! Data deleted (if it existed) at: secret/app/web
vault kv get secret/app/web
---
Key Value
--- -----
created_time 2022-12-15T17:41:41.13052Z
deletion_time 2022-12-15T17:42:03.369955Z
destroyed false
version 3
- Permanent deletion (KV v2)
- Use destroy to remove data irreversibly (restorable only via Vault/Consul backup)
Encrypting Data With the Transit Secrets Engine
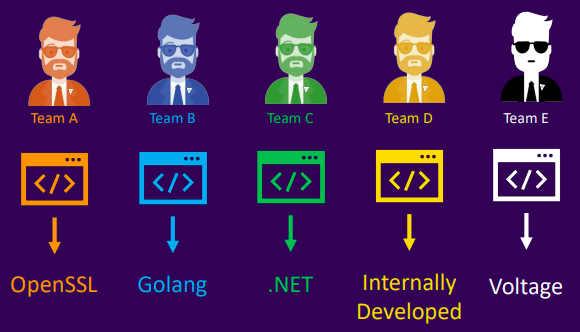
Challenges with enterprise encryption
- Options
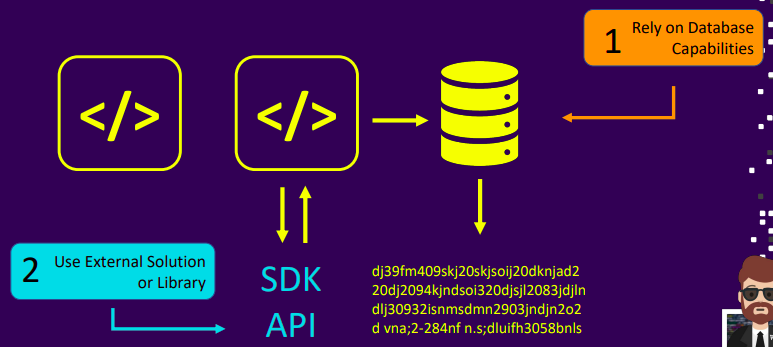
- Database choice
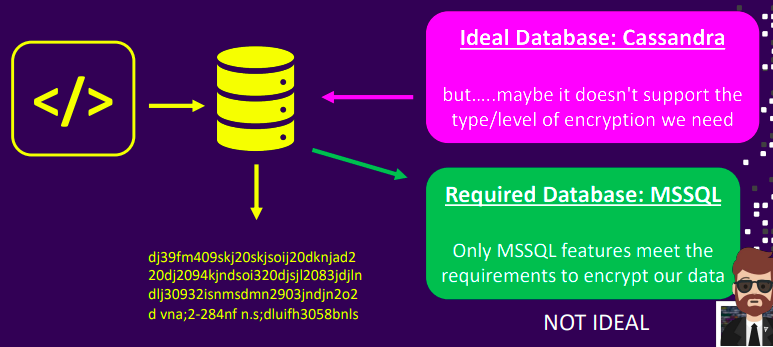
- Developer burden
Solutions
- Transit secrets engine: Centralizes encryption
- Organizational benefit: Streamlines encryption needs

Intro to Transit Secrets Engine
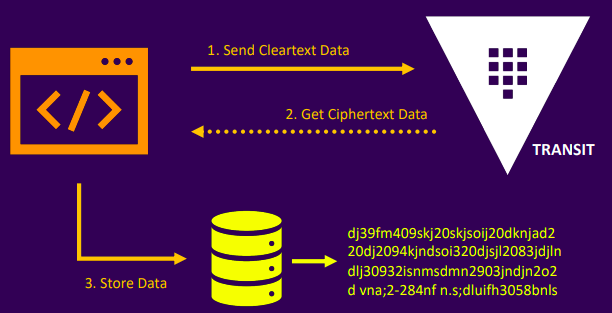
- Provides encryption/decryption services, centralizing organizational encryption
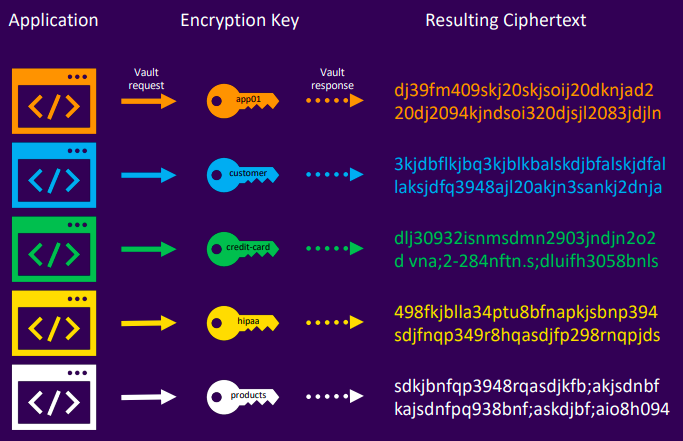
- Apps send plaintext to Vault, receiving ciphertext without accessing keys
- Keys are Vault-managed, with per-app key support and policy-based access
- Features
- Key rotation with versioned keyrings
- Restrict decryption to specific key versions
- Rewrap ciphertext to newer keys
- Convergent encryption for consistent ciphertext output
note
Plaintext must be base64-encoded (not encryption); Transit does not store encrypted data
Encryption key types
| Key Type | Description |
|---|---|
| aes128-gcm96 | 128-bit AES-GCM, 96-bit nonce; supports encryption, decryption, derivation, convergent mode. |
| aes256-gcm96 | 256-bit AES-GCM, 96-bit nonce; default, same support as above. |
| chacha20-poly1305 | 256-bit ChaCha20-Poly1305; same support as above. |
| ed25519 | Ed25519; supports signing, verification, derivation. |
| ecdsa-p256 | ECDSA P-256; supports signing, verification. |
| ecdsa-p384 | ECDSA P-384; supports signing, verification. |
| ecdsa-p521 | ECDSA P-521; supports signing, verification. |
| rsa-2048 | 2048-bit RSA; same support as above. |
| rsa-3072 | 3072-bit RSA; same support as above. |
| rsa-4096 | 4096-bit RSA; same support as above. |
Using the Transit Secrets Engine
Enable the engine
vault secrets enable transit
---
Success! Enabled the transit secrets engine at: transit/
Create an encryption Key
vault write -f transit/keys/vault_training
---
Success! Data written to: transit/keys/vault_training
- Specify key type
vault write -f transit/keys/training_rsa type="rsa-4096"
---
Success! Data written to: transit/keys/training_rsa
Encrypt data
vault write transit/encrypt/training \
plaintext=$(base64 <<< "Getting Started with HashiCorp Vault")
---
Key Value
--- -----
ciphertext vault:v1:Fpyph6C7r5MUILiEiFhCoJBxelQbsGeEahal5LhDPSoN6HkTOhwn79DCwt0mct1ttLokqikAr0PAopzm2jQAKJg=
key_version 1
Decrypt data
vault write transit/decrypt/training \
ciphertext="vault:v1:Fpyph6C7r5MUILiEiFhCoJBxelQbsGeEahal5LhDPSoN6HkTOhwn79DCwt0mct1ttLokqikAr0PAopzm2jQAKJg="
---
Key Value
--- -----
plaintext R2V0dGluZyBTdGFydGVkIHdpdGggSGFzaGlDb3JwIFZhdWx0Cg==
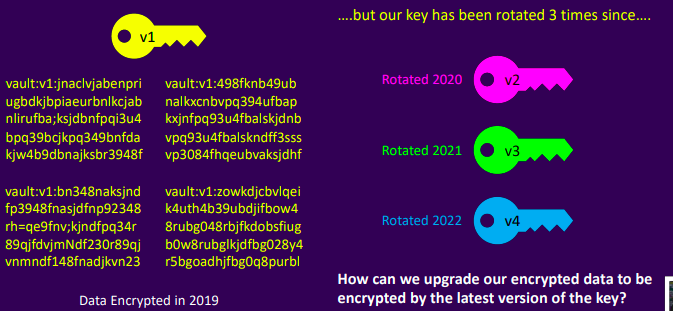
Rotate a Key
vault write transit/decrypt/training \
ciphertext="vault:v1:Fpyph6C7r5MUILiEiFhCoJBxelQbsGeEahal5LhDPSoN6HkTOhwn79DCwt0mct1ttLokqikAr0PAopzm2jQAKJg="
---
Key Value
--- -----
plaintext R2V0dGluZyBTdGFydGVkIHdpdGggSGFzaGlDb3JwIFZhdWx0Cg==
- Check key versions
vault read transit/keys/training
---
Key Value
--- -----
keys map[1:1647960245 2:1647960257 3:1647961177]
latest_version 3
min_decryption_version 1
type aes256-gcm96
Set minimum decryption version


vault write transit/keys/training/config min_decryption_version=4
---
Success! Data written to: transit/keys/training/config
- Verify configuration
vault read transit/keys/training
---
Key Value
--- -----
keys map[4:1647962305]
latest_version 4
min_decryption_version 4
type aes256-gcm96
Rewrap Ciphertext
vault write transit/rewrap/training \
ciphertext="vault:v1:Fpyph6C7r5MUILiEiFhCoJBxelQbsGeEahal5LhDPSoN6HkTOhwn79DCwt0mct1ttLokqikAr0PAopzm2jQAKJg="
---
Key Value
--- -----
ciphertext vault:v4:RFzp1kMpjtUIiS+6qxrNjIJEdPqCepFUa2ivr70…
key_version 4