compare authentication methods
Intro to Auth Methods
Key features
- Performing authentication and managing identities
- Assigning identities and associated policies to users
- Supporting multiple methods tailored to specific use cases
- Human-oriented: LDAP, OIDC, etc.
- System-oriented: AppRole, AWS, etc.
- Once authenticated, Vault issues a client token used for all subsequent requests (e.g., read/write operations)
- The primary goal of all authentication methods is to obtain a token
- Each token is linked to one or more policies and has a time-to-live (TTL)
Tokens in Vault
- Tokens are the core authentication mechanism in Vault
- Most Vault operations require a valid token
- The token auth method creates and manages tokens
- Enabled by default and cannot be disabled
- External authentication (e.g., LDAP, OIDC) generates a Vault token
- If a token is not provided for non-authentication requests, Vault returns a 403 Access Denied error without redirects or hints
Workflow
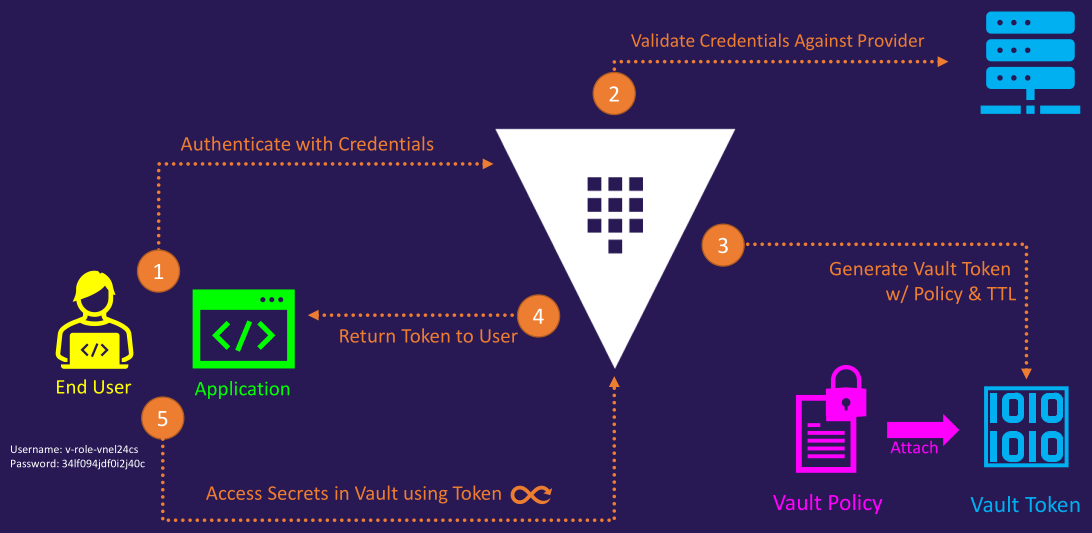
Working With Auth Methods
Key features
- Most auth methods must be explicitly enabled before use
- Multiple auth methods can coexist, often serving distinct purposes (e.g., applications vshuman users)
- The token auth method is always enabled
- A new Vault deployment relies on a root token for initial authentication
- It cannot be disabled or replaced as the sole method in a fresh setup
Auth methods can be enabled, disabled, or configured via
- Vault UI (limited functionality compared to CLI/API)
- Vault API
- Vault CLI
Requirement
- A valid token with sufficient privileges is needed to manage auth methods
Path configuration
- Each auth method is enabled at a specific path
- Custom paths can be set when enabling the method (only at creation)
- If unspecified, the default path matches the method type (e.g., aws for AWS, approle for AppRole)
vault auth enable approle
---
Success! Enabled approle auth method at: approle/
Configuring Auth Methods Using CLI
Use the vault auth comamnd
- enable
- disable
- list
- tune
- help
CLI commands for authentication
- Enabling and disabling auth methods
vault auth enable approle
---
Success! Enabled approle auth method at: approle/
vault auth disable approle
---
Success! Disabled the auth method (if it existed) at: approle/
vault auth list
---
Path Type Accessor Description
---- ---- -------- -----------
kyphan/ approle auth_approle_d8c20abe n/a
token/ token auth_token_89ce3371 token-based credentials
vault-course/ approle auth_approle_b3f0c92d n/a
- Custom paths and descriptions
- Enable
- Syntax:
vault <object_type> <subcommand> <customize> <description> <method_type>
- Syntax:
- Disable
- Syntax:
vault <object_type> <subcommand> <object_path>
- Syntax:
- Enable
vault auth enable approle
---
Success! Enabled approle auth method at: approle/
vault auth enable -path=vault-course approle
---
Success! Enabled approle auth method at: vault-course/
vault auth enable -path=apps -description="MyApps" approle
vault auth disable apps
Configuring auth methods
- Syntax:
vault write auth/<path_name>/<option>
vault write auth/approle/role/vault-course \
secret_id_ttl=10m \
token_num_uses=10 \
token_ttl=20m \
token_max_ttl=30m \
secret_id_num_uses=40
Configuring Auth Methods Using API
Vault provides a fully-featured API designed for machine-to-machine interaction
Critical components of an API request that need to be included
- Request Type: GET, POST, or DELETE
- Headers: Appropriate headers such as X-Vault-Token, Authorization, or X-Vault-Namespace
- Data: Included if required by the request
- API Endpoint: Specifies the Vault component being interacted with
HTTP API: When is a token required?
- Using an Auth Method: When authenticating to Vault via the API, a token is not required because authentication generates a new token
- Configuring an Auth Method: When enabling, configuring, or disabling an authentication method, a token with appropriate permissions must be provided
Enabling an authentication method
- Method: POST
curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ" \
--request POST \
--data '{"type": "approle"}' \ # Can reference a file, e.g., --data @data.json
https://vault.example.com:8200/v1/sys/auth/approle # API endpoint
Vault Authentication Using CLI
Vault offers several ways to authenticate via the command-line interface (CLI)
Using the vault login command
- Authenticate using a token or another authentication method
- Utilizes a token helper to store the token
- Syntax:
vault login -method=<method_type> <argument>
Example: Token-based authentication
vault login <hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ>
---
Success! You are now authenticated. The token information displayed below is
already stored in the token helper. You do NOT need to run "vault login" again
Future Vault requests will automatically use this token
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
token_accessor 502YCRmp1SfZ8YCdfbYeS9fj
token_duration ∞
token_renewable false
token_policies ["root"]
identity_policies []
policies ["root"]
Example: Userpass authentication
vault login -method=userpass username=kyphan
---
Password (will be hidden)
Success! You are now authenticated. The token information displayed below
is already stored in the token helper. You do NOT need to run "vault login"
again. Future Vault requests will automatically use this token
Key Value
--- -----
token hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
token_accessor SpiJi6bghz4huS8MG4HsLmNp
token_duration 768h
token_renewable true
token_policies ["admin", "default"]
identity_policies []
policies ["admin", "default"]
token_meta_username kyphan
Use the VAULT_TOKEN environment variable
- Use this method if you already have a token
Token Helper
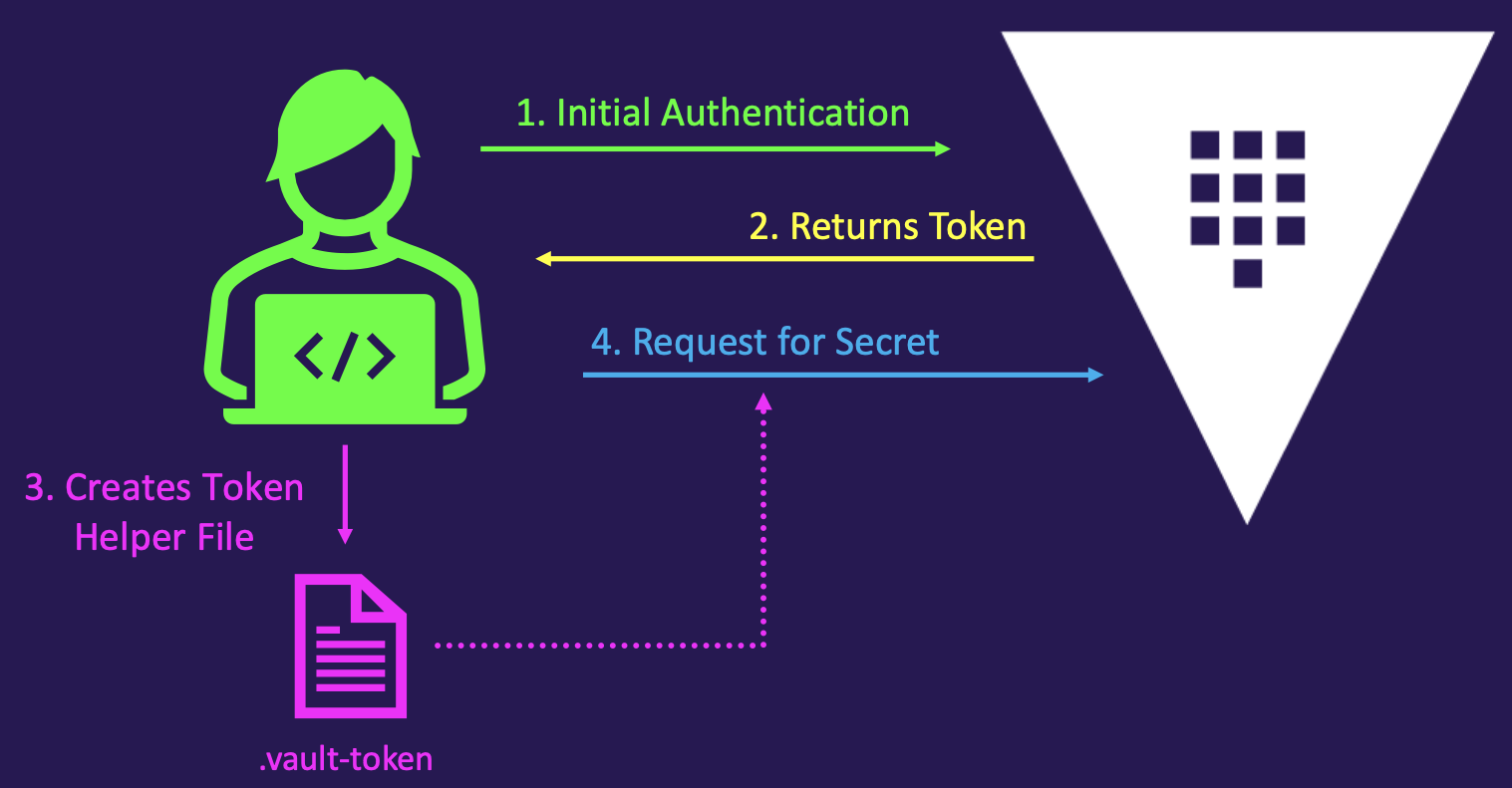
- Caches the token after authentication and stores it in a local file -
.vault-tokenfor use in subsequent requests
Parsing the JSON response to obtain the Vault token
export VAULT_ADDR="https://vault.example.com:8200"
export VAULT_FORMAT=json
OUTPUT=$(vault write auth/approle/login role_id="12345657" secret_id="1nv84nd3821s")
VAULT_TOKEN=$(echo "$OUTPUT" | jq '.auth.client_token' -j)
vault login "$VAULT_TOKEN"
Vault Authentication Using API
Authentication requests to the Vault HTTP API return a JSON response that include
- The token
- The token accessor
- Information about attached policies
Users must parse the response to extract the token and use it for subsequent Vault requests
Authenticating with an authentication method
- Data: Role_id, secret_id, etc.
- Method: POST
- Response: JSON
curl \
--request POST \
--data @auth.json \
https://vault.example.com:8200/v1/auth/approle/login
---
{
"request_id": "0f874bea-16a6-c3da-8f20-1f2ef9cb5d22",
"lease_id": "",
"renewable": false,
"lease_duration": 0,
"data": null,
"wrap_info": null,
"warnings": null,
"auth": {
"client_token": "hvs.wjkffdrqM9QYTOYrUnUxXyX6",
"accessor": "Hbhmd3OfVTXnukBv7WxMrWld",
"policies": ["admin", "default"],
"metadata": {}
}
}
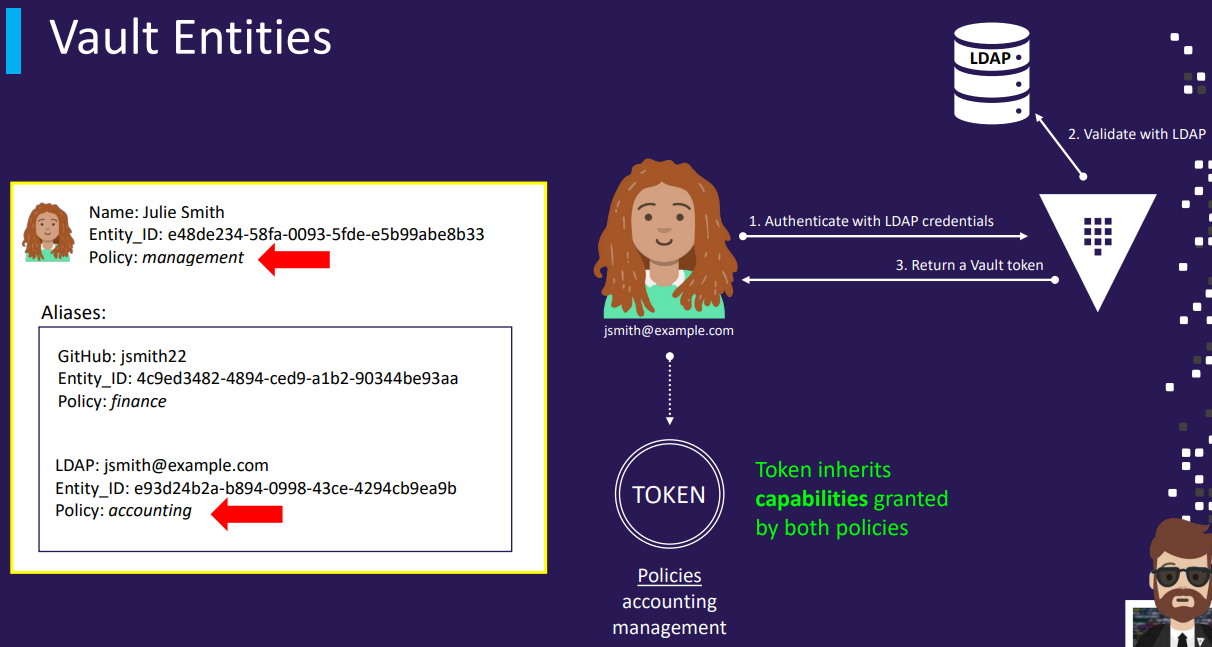
Vault Entities
Key features
- Vault creates an entity and attaches an alias to it if a corresponding entity does not already exist
- This is managed through the identity secrets engine, which oversees internal identities recognized by Vault
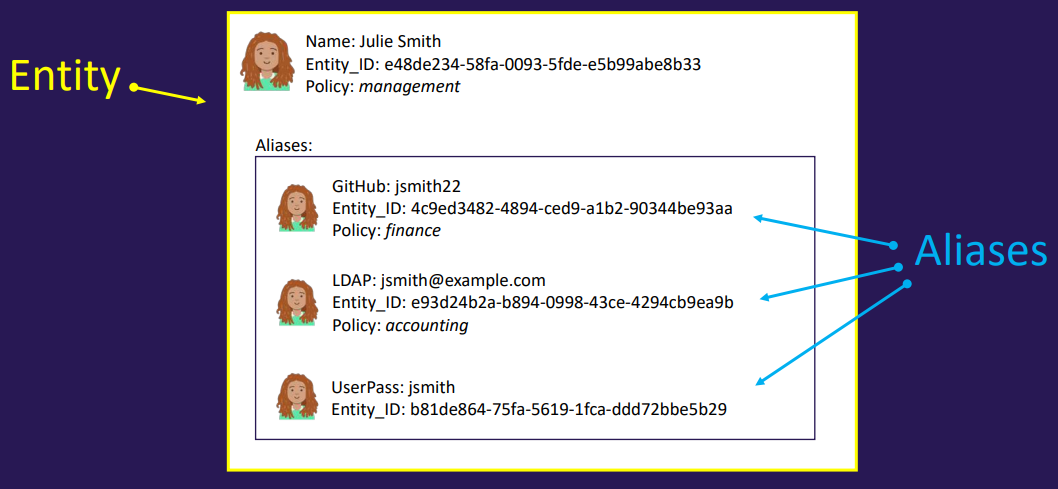
- An entity represents a single person or system that logs into Vault. Each entity has a unique identifier and consists of zero or more aliases
- An alias is a combination of an authentication method and an identifier. It serves as a mapping between an entity and one or more authentication methods
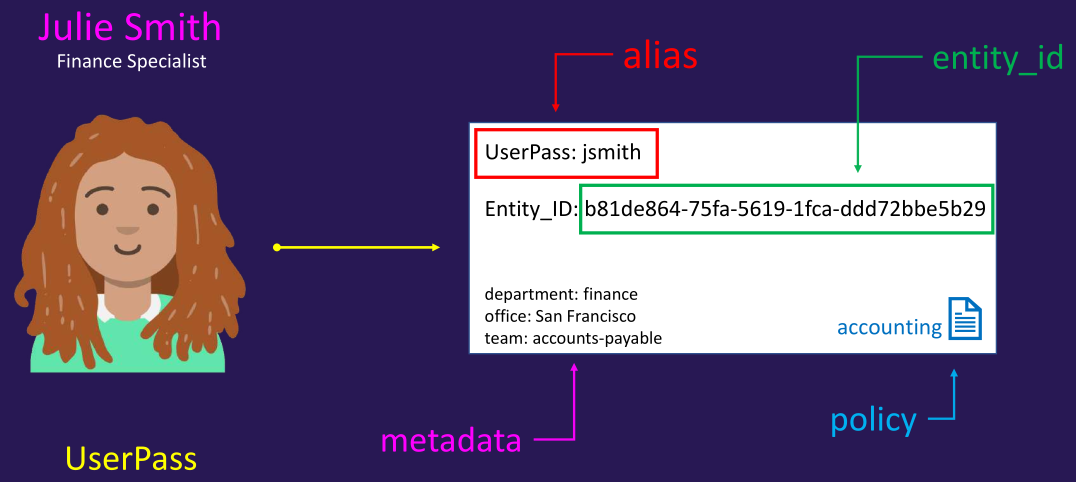
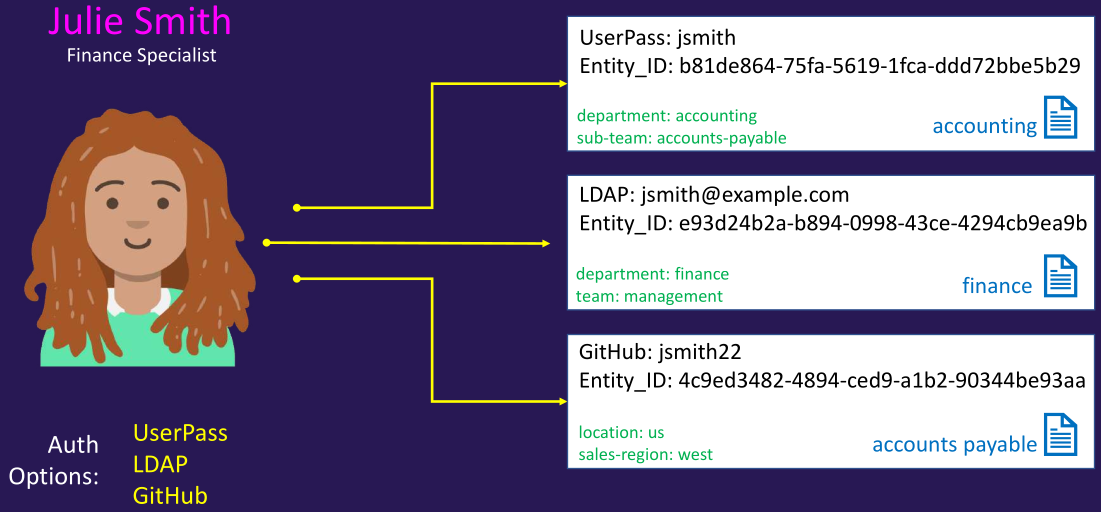
- Entities can be manually created to consolidate multiple aliases for a single user, enabling more efficient authorization management
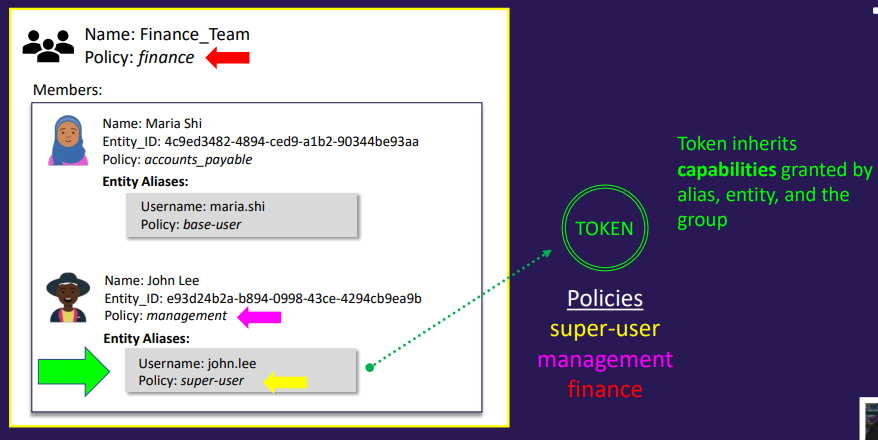
- Tokens created for an entity inherit the capabilities granted by its associated alias(es)
Workflow
Vault Identity Groups
Key features
- A group can include multiple entities as its members
- A group can also contain subgroups
- Policies applied to a group grant permissions to all its members

Types of groups
- Internal group
- Groups created within Vault to organize entities and propagate identical permissions
- Created manually
- Simplify permission management for entities
- They are commonly used with Vault Namespaces to propagate permissions to child namespaces
- This is particularly useful when you want to avoid configuring identical authentication methods for every namespace
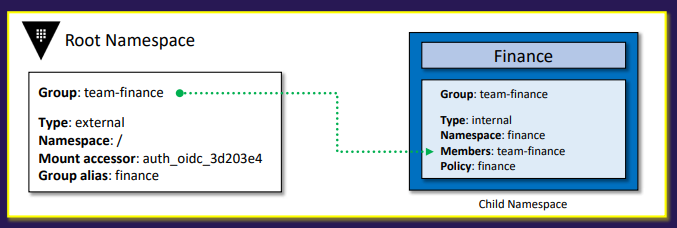
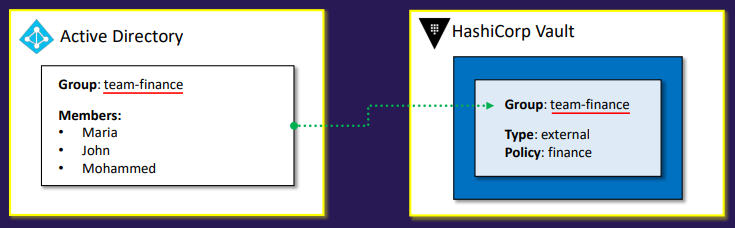
- External group
- Groups that Vault infers and creates based on group associations from authentication methods
- Created manually or automatically
- External groups allow permissions to be set based on group membership from an external identity provider, such as LDAP, Okta, or an OIDC provider
- This enables a one-time setup in Vault, with ongoing permission management handled in the identity provider
- Note: The group name in Vault must match the group name in the identity provider
Choosing an Auth Method
When selecting an authentication method, consider the following key factors and their implications
- Frequently rotated
- Typically refers to dynamic credentials that are regularly updated
- Meets the requirements: AWS, LDAP, Azure, GCP (Google Cloud Platform), Kubernetes (K8s)
- Does not meet the requirements: Userpass, TLS Certificates, AppRole
- Remove secrets from process or build pipeline
- Generally indicates the use of dynamic or integrated credentials to eliminate hardcoded secrets
- Meets the requirements: AWS, Azure, GCP (Google Cloud Platform), Kubernetes (K8s)
- Does not meet the requirements: Userpass, LDAP
- Use existing user credentials
- Typically means integrating with an existing identity provider to leverage current user credentials
- Meets the Requirement: OIDC (OpenID Connect), LDAP, Okta, GitHub
- Does not meet the requirements: Userpass, AWS, Azure, GCP (Google Cloud Platform)
Differentiate Human vs. System Auth Methods
Vault supports a wide variety of authentication methods, which can be broadly categorized into those designed for human-based authentication and those intended for machine-to-machine (system-based) authentication
Human-based auth methods
- Integrates with an existing identity provider
- Requires a hands-on approach to use
- Involves logging in via a prompt or pop-up
- Often configured with the platform's integrated multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Example: GitHub, JWT/OIDC, Okta, RADIUS, userpass
System-based auth emthods
- Utilizes methodologies that are not human-friendly (e.g., difficult-to-remember credentials)
- Typically integrates with an existing backend platform
- Vault validates credentials directly with the platform
- Example: AWS, Tokens, Cloud Foundry, TLS Certificates, Kerberos, Microsoft Azure, AppRole, Oracle Cloud, GCP (Google Cloud Platform), Alibaba Cloud, Kubernetes (K8s)
Demo
Configuring Auth Methods Using CLI
vault auth -h
vault auth enable userpass
vault auth list
vault auth enable -path=vault-course userpass
vault auth list
vault auth disable userpass
vault auth list
vault disable vault-course
vault auth enable -path=kyphan -description="local credentials for Vault" userpass
vault auth list
vault auth tune -default-lease-ttl=24h kyphan/
vault write auth/kyphan/users/andy password=vault policies=kyphan
vault list auth/kyphan/users/andy
vault read auth/kyphan/users/andy
vault auth enable approle
vault write auth/approle/role/kyphan token_ttl=20m policies=kyphan
Configuring Auth Methods Using API
curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ" \
--request POST \
--data @auth.json \
http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/sys/auth/approle
vault auth list
curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ" \
--request POST \
--data @policies.json \
http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/approle/role/vaultcourse
curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ" \
http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/approle/role/vaultcourse/role-id | jq
curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ" \
-- request POST \
http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/approle/role/vaultcourse/secret-id | jq
Configuring Auth Methods Using UI
Directions: Homepage → Access → Enable new method
vault login -method=username username=kyphan password=kp123
Vault Authentication Using CLI
vault login -method=okta [email protected] password=kp123
vault auth enable aws
vault auth disable aws
vault policy list
vault write auth/approle/roles/login role_id=asd123 secret_id=qwe123
vault login -method=userpass username=kyphan password=kp123
Vault Authentication Using API
curl \
--request POST \
--data @password.json \
http://1270.0.0.1:8200/v1/auth/okta/login/[email protected] | jq
curl \
--header "X-Vault-Token: hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ" \
http://127.0.0.1:8200/v1/secret/data/app01 | jq
Vault Authentication Using UI
Directions: Homepage → Profile
vault login <token>
export VAULT_TOKEN=hvs.2kjqZ12ofDr3efPdtMJ1z5dZ
AppRole Auth Method
Setup
vault auth list
vault auth enable approle
vault write auth/approle/role/kyphan pocilies=kyphan token_ttl=20m
vault list auth/approle/role
vault read auth/approle/role/kyphan/role-id
vault write -f auth/approle/role/kyphan/secret-id
Login
vault write auth/approle/login role_id=<role_id> secret_id=<secret_id>
Okta Auth Method
Setup
- Directions: Homepage → Security → API → Tokens → Create Token
vault auth enable okta
vault auth list
vault write auth/okta/config base_url="okta.com" org_name="kyphan" api_token="<token>"
vault read auth/okta/config
vault write auth/okta/users/[email protected] policies=kyphan
Login via UI
- Method: Okta
- Username:
<[email protected]> - Password:
<okta_password>
Login via CLI
vault login -method=okta [email protected]
UserPass Auth Method
Setup
vault auth list
vault auth enable userpass
vault write auth/userpass/users/kyphan password=kp policies=kyphan
vault write auth/userpass/users/kyphann password=kpp policies=kyphan
vault list auth/userpass/users
vault read auth/userpass/users/kyphan
Login
vault login -method=userpass username=kyphan password=kp
vault login -method=userpass username=kyphann password=kpp